ATP binding domain 4 Introductions: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
We have been assigned to investigate ATP Binding Domain 4 (1ru8A) which is a N-type ATP pyrophosphatase from ''Pyrococcus furiosus''.It was found that ATP pyrophosphatase involved in hydrolyzing the phosphodiester bond in ATP. N-type ATP pyrophosphatase is a family belongs to the superfamily- Adenine Nucleotide Alpha Hydrolases-like (AANH-like). Other members of AANH-like are arginosuccinate synthase, NAD synthase, GMP synthase and tRNA Methyl transferase. All these family members contain highly conserved PP-loop which is likely to be involved in phosphate binding. This motif is a modified form of P-loop of nucleotide binding domains. PP-loop consists of conserved motif SGGKD at the N terminus. These sequences are highly conserved among all the family members (See '''Diagram 2''') and across all species in domain Archaea and Eukarya. However the sequence similarity is very low compared to that for bacteria. Based on the comparison between other family members such as arginosuccinate synthase, the function of ATP binding Domain 4 can be inferred. The function can be inferred based on the similarity of the structure and evolution of the amino acid sequences. | We have been assigned to investigate ATP Binding Domain 4 (1ru8A) which is a N-type ATP pyrophosphatase from ''Pyrococcus furiosus''.It was found that ATP pyrophosphatase involved in hydrolyzing the phosphodiester bond in ATP (see Diagram 1). N-type ATP pyrophosphatase is a family belongs to the superfamily- Adenine Nucleotide Alpha Hydrolases-like (AANH-like). Other members of AANH-like are arginosuccinate synthase, NAD synthase, GMP synthase and tRNA Methyl transferase. All these family members contain highly conserved PP-loop which is likely to be involved in phosphate binding. This motif is a modified form of P-loop of nucleotide binding domains. PP-loop consists of conserved motif SGGKD at the N terminus. These sequences are highly conserved among all the family members (See '''Diagram 2''') and across all species in domain Archaea and Eukarya. However the sequence similarity is very low compared to that for bacteria. Based on the comparison between other family members such as arginosuccinate synthase, the function of ATP binding Domain 4 can be inferred. The function can be inferred based on the similarity of the structure and evolution of the amino acid sequences. | ||
Since ATP Binding Domain 4 is less well-studied compared to other members of the clan PP-loop, it becomes an interest to investigate the evolution, structure and function of the protein. The structure of this protein has been resolved by X-ray crystallography but the function and the substrates remain unknown. The approach that we used to determine the function is based on structural similarity. By comparing the mechanisms with structurally related proteins, the function of ATP Binding Domain 4 can be deduced. | Since ATP Binding Domain 4 is less well-studied compared to other members of the clan PP-loop, it becomes an interest to investigate the evolution, structure and function of the protein. The structure of this protein has been resolved by X-ray crystallography but the function and the substrates remain unknown. The approach that we used to determine the function is based on structural similarity (see diagram 2).By comparing the mechanisms with structurally related proteins, the function of ATP Binding Domain 4 can be deduced. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
'''Diagram 2.''' Summary of enzymes containing the PP-loop motif. Adapted from Bork. P.& Koonin, E.V. | '''Diagram 2.''' Summary of mechanisms of enzymes containing the PP-loop motif which is the only conserved region in multiple sequence alignment. Adapted from Bork. P.& Koonin, E.V. | ||
[[ATP binding domain 4 | Back to Main ATP binding domain 4 pages]] | [[ATP binding domain 4 | Back to Main ATP binding domain 4 pages]] | ||
Bork, P & Koonin, E.V. (1994), A P-Loop-Like Motif in a Widespread ATP Pyrophosphatase Domain: Implications for the Evolution of Sequence Motifs and Enzyme Activity, Proteins: Structure, Function and Genetics, 20, 347-355. | Bork, P & Koonin, E.V. (1994), A P-Loop-Like Motif in a Widespread ATP Pyrophosphatase Domain: Implications for the Evolution of Sequence Motifs and Enzyme Activity, Proteins: Structure, Function and Genetics, 20, 347-355. | ||
Revision as of 06:27, 5 June 2009
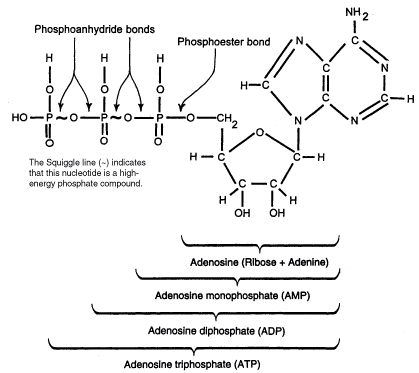
ATP consists of adenosine nucleotide linked to 3 phosphate groups. The third phosphate group of ATP can be removed by hydrolysis thus releasing free energy making it a major energy currency of the cell. ATP can be consumed by cells which undergo anabolic reaction such as cell division, active transport and muscle contraction.
Diagram 1.ATP cleavage.
We have been assigned to investigate ATP Binding Domain 4 (1ru8A) which is a N-type ATP pyrophosphatase from Pyrococcus furiosus.It was found that ATP pyrophosphatase involved in hydrolyzing the phosphodiester bond in ATP (see Diagram 1). N-type ATP pyrophosphatase is a family belongs to the superfamily- Adenine Nucleotide Alpha Hydrolases-like (AANH-like). Other members of AANH-like are arginosuccinate synthase, NAD synthase, GMP synthase and tRNA Methyl transferase. All these family members contain highly conserved PP-loop which is likely to be involved in phosphate binding. This motif is a modified form of P-loop of nucleotide binding domains. PP-loop consists of conserved motif SGGKD at the N terminus. These sequences are highly conserved among all the family members (See Diagram 2) and across all species in domain Archaea and Eukarya. However the sequence similarity is very low compared to that for bacteria. Based on the comparison between other family members such as arginosuccinate synthase, the function of ATP binding Domain 4 can be inferred. The function can be inferred based on the similarity of the structure and evolution of the amino acid sequences.
Since ATP Binding Domain 4 is less well-studied compared to other members of the clan PP-loop, it becomes an interest to investigate the evolution, structure and function of the protein. The structure of this protein has been resolved by X-ray crystallography but the function and the substrates remain unknown. The approach that we used to determine the function is based on structural similarity (see diagram 2).By comparing the mechanisms with structurally related proteins, the function of ATP Binding Domain 4 can be deduced.
Diagram 2. Summary of mechanisms of enzymes containing the PP-loop motif which is the only conserved region in multiple sequence alignment. Adapted from Bork. P.& Koonin, E.V.
Back to Main ATP binding domain 4 pages
Bork, P & Koonin, E.V. (1994), A P-Loop-Like Motif in a Widespread ATP Pyrophosphatase Domain: Implications for the Evolution of Sequence Motifs and Enzyme Activity, Proteins: Structure, Function and Genetics, 20, 347-355.