Result of SNAPG: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 75: | Line 75: | ||
=== Background === | === Background === | ||
[[Image:Cladogram view.JPG]] | [[Image:Cladogram view.JPG|left|500px|]] | ||
-> This is the cladogram treeview of SNAP-gamma protein. However, this view is not suitable enough to represent the evolutionary gap between species but this is clearly shows the species name. | -> This is the cladogram treeview of SNAP-gamma protein. However, this view is not suitable enough to represent the evolutionary gap between species but this is clearly shows the species name. | ||
=== Final Tree Analysis === | === Final Tree Analysis === | ||
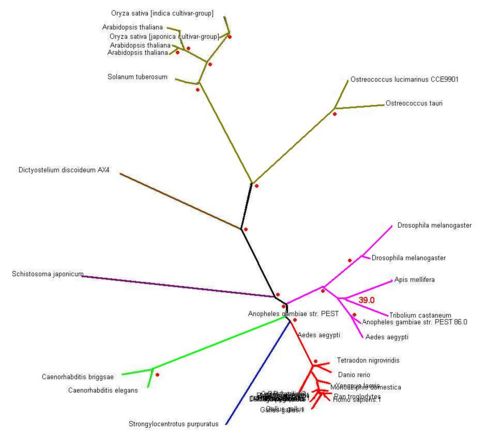
[[Image:Rad.JPG]] | [[Image:Rad.JPG|left|500px|]] | ||
-> Evolutionary analysis of the tree with radial view (for professional viewer) | -> Evolutionary analysis of the tree with radial view (for professional viewer) | ||
Revision as of 09:41, 11 June 2007
SNAPG Structure
Structure architecture
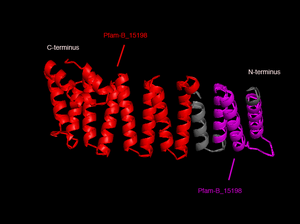
In order to analyze protein structure of SNAPG, structural comparison to known protein structure is required. An insight to SNAPG structural arrangement provides various informative data on possible protein functions and interactions with another protein and/or DNA. Based on protein families database, Pfam at Sanger, it was found that SNAPG protein matched to Pfam-B protein families and consist of 2 domains, Pfam-B_7270 (PB007270) and Pfam-B_15198 (PB015189) respectively as shown in Figure 3. Both of 2 domains appears to be associated with NSF attachment protein activity (*dijelasin di discussion aja! NSF acivity dijelasin ga?)[1].

. The sequence was also used against InterproScan generated by Profunc that gave an TFR (Tetratricopeptide-like helical) domain classification while that of protein family agrees with Pfam classification.
(interproscan)
Structural comparison
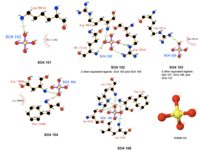
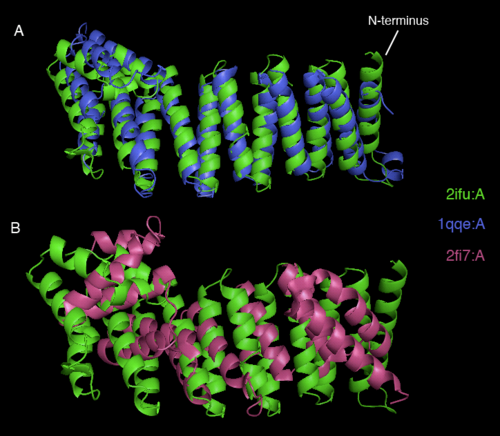
Dali webserver is one of the powerful tool to screen any protein that are structurally homologous with our query. Two structurally related proteins with highest Z-value generated by Dali server were chosen for SNAPG structure comparison analysis. These proteins were vesicular transport ptotein sec17 (1qqe) and type 4 fimbrial biogenesis protein (2f17) (refer to Table 1).alto
| PDB-chain | Structure | Z-value | % identity | Protein |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2IFU-A | 37.8 | 100 | Endocytosis/exocytosis. Gamma-SNAP (Danio rerio) | |
| 1QQE-A | 23.3 | 23 | Protein binding. Vesicular transport protein sec17(yeast) | |
| 2FI7-A | 12.9 | 14 | Protein transport. Type 4 fimbrial biogenesis protein pili (Pseudomonas aeruginosa) |
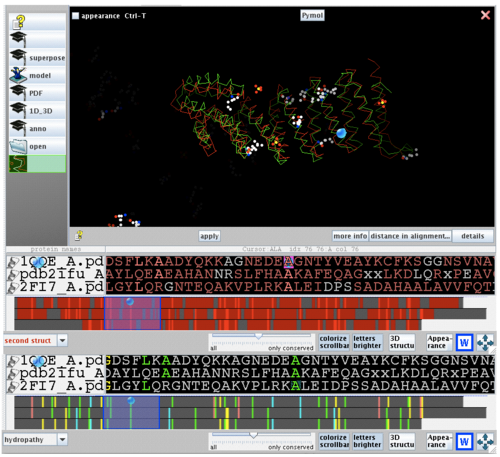
2ifuA, 1qqeA and 2fi7 alignment
physical properties
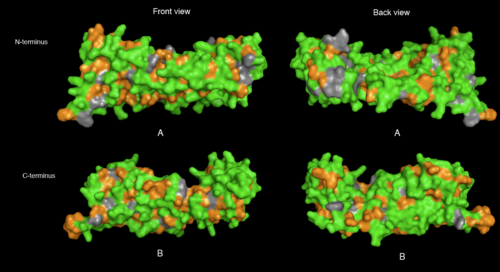
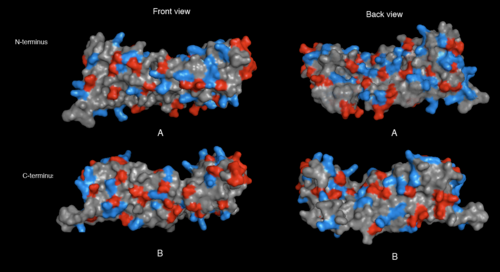
[[image:Electrostatic potential (molecular surface).png|thumb|left|500px|Figure 9. 2ifuA electrostatic potential map visualised by molecular surface. Computation method that were used are coulumb method.](red= -1.800; white= 0.000; blue= +1.800]
Figure 10 cleft
SNAPG Function
Function by Similarity
SNAPG Evolution
Background
-> This is the cladogram treeview of SNAP-gamma protein. However, this view is not suitable enough to represent the evolutionary gap between species but this is clearly shows the species name.
Final Tree Analysis
-> Evolutionary analysis of the tree with radial view (for professional viewer)
Legends:
- Red-dotted sign means boostrap value more than 75.00 or 75%
- any number (in red) located near branching tree indicated boostrap value of the branching tree
- Green Line: The species belongs to Plants group
- Brown Line: Amoeba group
- Purple Line: Parasite type
- Pink Line : The species belongs to Insects Group
- Light Green Line: Worms Group
- Dark Blue Line: Invertebrate
- Red Line: Vertebrate
Other version: Evolutionary analysis of the tree with radial view (for non-professional or common viewer)
Understanding the Tree
SNAP-gamma protein evolutionary tree mostly contains more than 75% boostrapvalue. Thus, red dot signs was assign to represent more than 75% boostrap value. The value was indicated the degree of confidence about the branching order. As an example: in the diagram above, there is 39.0 boostrap value in branching Apis melifera and Tribolium castaneum. The boostrap value is below 75%, thus it could be concluded that the degree of confidence of branching tree in the correct order is far below 95%. On the other hand, boostrap value more than 75% or 75.00 means 95% confidence that the branching tree is in the correct order
As indicated in diagram above, SNAP-gamma protein was evolved in eukaryotes. There is no prokaryotes detected in the phylogenetic tree.
Function (in various organism) = nunggu justine
Thus, it could be concluded that SNAP-gamma protein is important protein in eukaryotes animal.