COASY results: Difference between revisions
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Appearance of Coenzyme A Synthase== | ==Appearance of Coenzyme A Synthase== | ||
Compared to other structurally related proteins, Coenzyme A Synthase in the Mus. Musculus has a number of conserved structural features, particularly in the inner contents of the protein (see Figure 5 and | Compared to other structurally related proteins, Coenzyme A Synthase in the Mus. Musculus has a number of conserved structural features, particularly in the inner contents of the protein (see Figure 5 and Figure 2). Major structural regions that are conserved are; the P-Loop (residues 75-90) of the first helix which is found in other proteins with the DPCK domain, the second helix, the second, third, fourth and fifth B-strands, and the eighth and eleventh helices (Figure 1). | ||
<BR> | <BR> | ||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
[[Image:COASYSecondary structure with bind sites.gif]]<BR> | [[Image:COASYSecondary structure with bind sites.gif]]<BR> | ||
'''Figure 1'''<BR> | '''Figure 1'''<BR> | ||
'''The secondary structure of Mus musculus with indicated ligand interaction sites (EMBL EBI, 2005).''' <BR> | |||
<image src = COASYStructureconservationstructurealignment.JPG >Structural alignment table of structurally related species</image><BR> | |||
'''Figure 2'''<BR> | |||
'''The secondary structure of Mus musculus with indicated ligand interaction sites (EMBL EBI, 2005).''' <BR> | '''The secondary structure of Mus musculus with indicated ligand interaction sites (EMBL EBI, 2005).''' <BR> | ||
Revision as of 06:25, 5 June 2007
Appearance of Coenzyme A Synthase
Compared to other structurally related proteins, Coenzyme A Synthase in the Mus. Musculus has a number of conserved structural features, particularly in the inner contents of the protein (see Figure 5 and Figure 2). Major structural regions that are conserved are; the P-Loop (residues 75-90) of the first helix which is found in other proteins with the DPCK domain, the second helix, the second, third, fourth and fifth B-strands, and the eighth and eleventh helices (Figure 1).
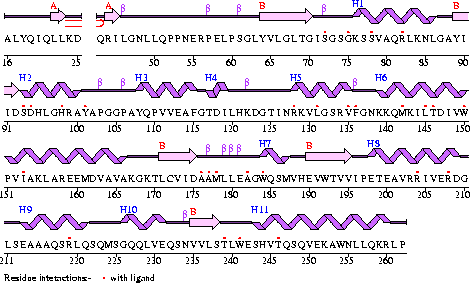
Figure 1
The secondary structure of Mus musculus with indicated ligand interaction sites (EMBL EBI, 2005).
<image src = COASYStructureconservationstructurealignment.JPG >Structural alignment table of structurally related species</image>
Figure 2
The secondary structure of Mus musculus with indicated ligand interaction sites (EMBL EBI, 2005).