Strucure Library: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 108: | Line 108: | ||
HSR1 is placed to the human MHC class I region. It is known to be highly homologous to a putative GTP binding protein like MMR1 from mouse. These are also known to represent a new subfamily of GTP binding proteins of prokaryote and eukaryote members. | HSR1 is placed to the human MHC class I region. It is known to be highly homologous to a putative GTP binding protein like MMR1 from mouse. These are also known to represent a new subfamily of GTP binding proteins of prokaryote and eukaryote members. | ||
[[Image:MG2 | [[Image:MG2.jpg]] | ||
[[Image:MG1.jpg]] | [[Image:MG1.jpg]] | ||
Revision as of 01:28, 12 June 2007
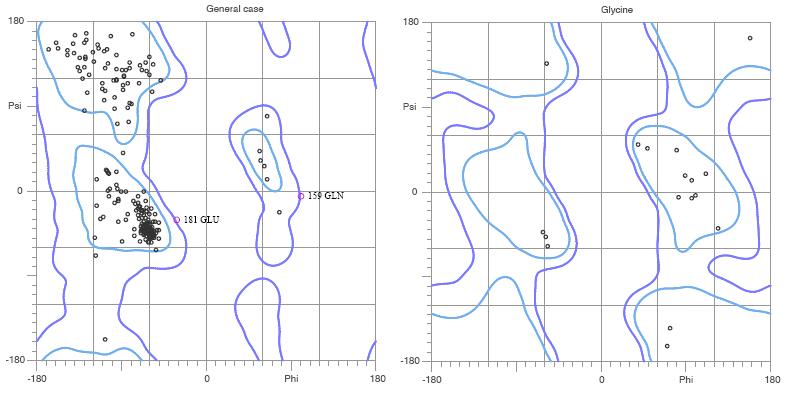
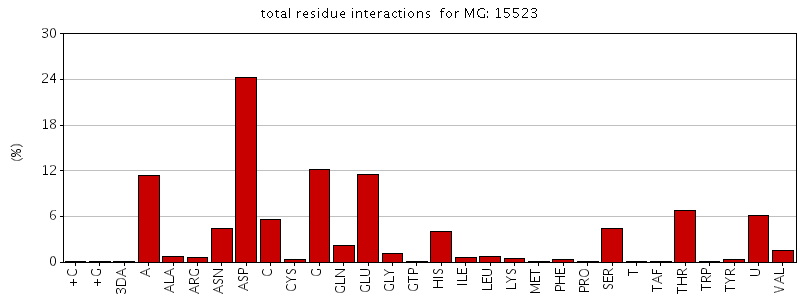
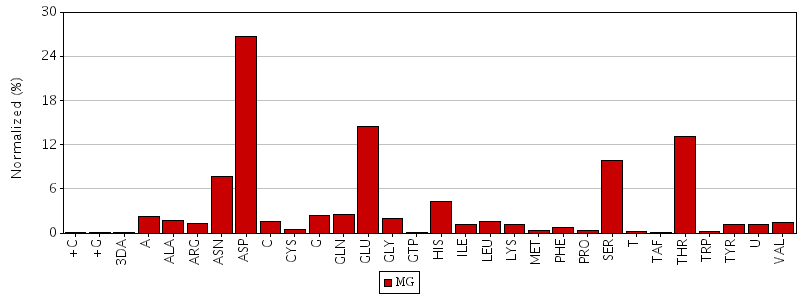
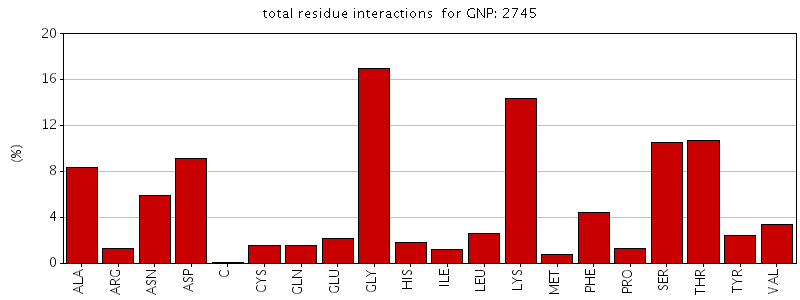
The asymmetric unit of Bacillus subtilis YlqF protein consists of a polymer containing 282 amino acids. It also contains ligands which are a magnesium ion and a Phosphoaminophosphonic acid-guanylate ester. The protein has been refined at 2 angstroms to a crystallographic R factor of 21.6% and free R factor of 25%. MolProbity Ramachandran analysis of YlqF shows that 96.5% of all residues lie in the favoured regions and 98.8% of all residues lie in the allowed regions.
| Parameters | Resolution[Å]
2.00 |
R factor, %
21.6 |
Free R factor, %
25.0 |
Space Group
P 21 21 21 |
| Unit Cell | Length[Å]
Angles [°] |
a
alpha |
36.75
90.00 |
b
beta |
68.57
90.00 |
c
gamma |
105.57
90.00 |
|---|
Table. Crystal parameters and refinement statistics
Figure. MolProbity Ramachandran analysis of YlqF
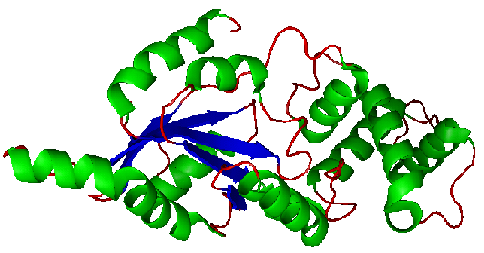
Figure. Structure of YlqF showing helix, sheet, and loop. Image was generated using the program PyMol (DeLano, 2002)
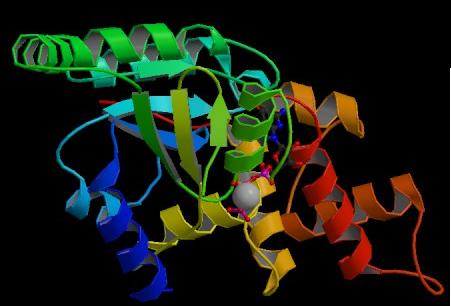
Figure. Structure of YlqF showing ligands. The image was obtained from PDB.
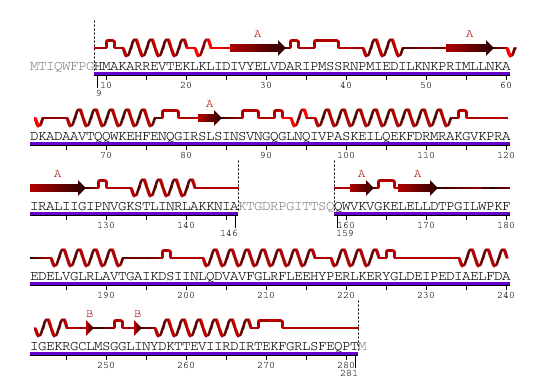
The secondary structure of YlqF mainly consists of 50% helix (13 helices; 142 residues) and 10% beta sheets (6 strands; 31 residues)(see Figure). YlqF protein consists of two domains (Figure). One domain contains Rossmann fold with α/β class. This domain possesses 1-177 residues, and forms a 3-layer sandwich structure. The other one is referred to as a conserved hypothetical protein with mainly α class. This possesses 178-282 residues, and forms a orthogonal bundle structure. YlqF is also classified as a signalling protein. The molecular weight of the protein is 31986 Da.
![]() = pi helix,
= pi helix, ![]() = 310 helix,
= 310 helix, ![]() = extended strand,
= extended strand, ![]() = turn,
= turn, ![]() = alpha helix,
= alpha helix,
Greyed out residues have no structural information
Figure 6. Sequence and Secondary Structure
Figure. Structure of YlqF showing two domains. Image was generated using the program PyMol (DeLano, 2002)
Structure classification of proteins (SCOP) classified YlqF. The results of Pfam classification described YlqF as GTPase of unknown function, Rhomboid family, and catalytic domain of alpha amylase.
| Class
Alpha and beta proteins |
Fold
P-loop containing nucleoside triphosphate hydrolases |
Superfamily
P-loop containing nucleoside triphosphate hydrolases |
Family
G proteins |
Domain
Probable GTPase YlqF |
Species
Bacillus subtilis |
InterProScan Results
InterPro: IPR005289 MG442 This is a GTP binding domain. This was found in many different families including Ras GTPase superfamily, HSR1-related GTP binding protein. And they all play different functions.
InterPro: IPR002917 MMR_HSR1 HSR1 is placed to the human MHC class I region. It is known to be highly homologous to a putative GTP binding protein like MMR1 from mouse. These are also known to represent a new subfamily of GTP binding proteins of prokaryote and eukaryote members.
Figure. Total residue interactions for magnesium ion
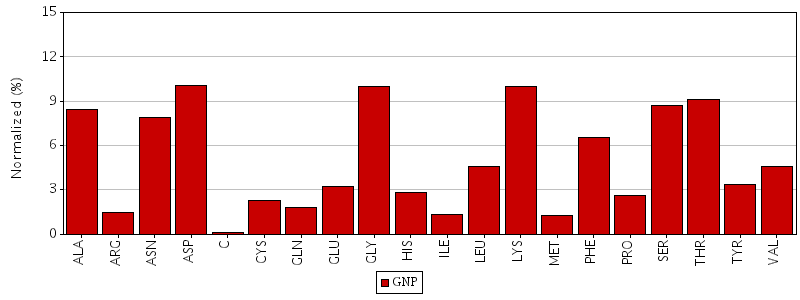
Figure. Total residue interactions for Phosphoaminophosphonic acid-guanylate ester (GNP)