Results (1zkd): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 372: | Line 372: | ||
After carefully analyzing the MSA in a clustal X format, the closest available sequence to the protein sequence of 1ZKD was the DUF185 protein sequence from Rhodopseudomonas palustris bacteria. The only differences were the occurrence of '''eight different amino acids''' randomly in the sequence and the '''eight extra amino acids''' at the 3’ end of the 1ZKD amino acid sequence. | After carefully analyzing the MSA in a clustal X format, the closest available sequence to the protein sequence of 1ZKD was the DUF185 protein sequence from Rhodopseudomonas palustris bacteria. The only differences were the occurrence of '''eight different amino acids''' randomly in the sequence and the '''eight extra amino acids''' at the '3’' or the 'C-terminus' end of the 1ZKD amino acid sequence. | ||
Our protein amino acid sequence is '''no. 32''' and the closest matched sequence is of DUF185 amino acid sequence is at '''no. 31'''. | Our protein amino acid sequence is '''no. 32''' and the closest matched sequence is of DUF185 amino acid sequence is at '''no. 31'''. | ||
=== Protdist === | === Protdist === | ||
Revision as of 03:11, 12 June 2007
Structure of Hypothetical Protein LOC55471 Isoform 1
Comparing Structure of Proteins
Dali Results
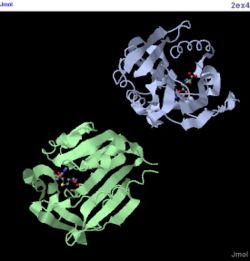
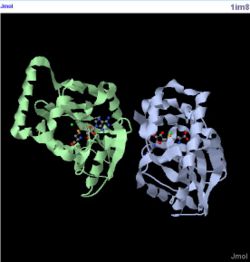
Dali shows a few proteins with similar structure to 1zkd. They are 2ex4 and 1im8 which shows the highest Z-value of 11.7 and 11.6 respectively. The higher the Z-value the more significant is the results. However, they are only 10-12% identical to the query protein. Nevertheless, these 2 proteins are used to compare with the query protein as these 10-12% identity may be at the binding site or ligand which will determine the functions. 2ex4 is a human methyltransferase with S-adenosylhomocysteine and 1im8 is found to be a methyltransferase with a bound S-adenosylhomocysteine from the crystal structure of YecO from Haemophilus influenzae (HI0319).
SUMMARY: PDB/chain identifiers and structural alignment statistics
NR. STRID1 STRID2 Z RMSD LALI LSEQ2 %IDE REVERS PERMUT NFRAG TOPO PROTEIN 1: 3027-A 1zkd-A 56.8 0.0 349 349 100 0 0 1 S STRUCTURAL GENOMICS, UNKNOWN FUNCTION duf185 (rhodops 2: 3027-A 2ex4-A 11.7 3.0 185 221 12 0 0 22 S TRANSFERASE adrenal gland protein ad-003 (homo sapien 3: 3027-A 1im8-A 11.6 3.2 178 225 10 0 0 18 S TRANSFERASE yeco (methyltransferase, hypothetical pro 4: 3027-A 2gb4-A 10.8 3.3 184 231 13 0 0 19 S TRANSFERASE thiopurine s-methyltransferase (thiopurine 5: 3027-A 2fk7-A 10.7 3.8 186 277 14 0 0 19 S TRANSFERASE methoxy mycolic acid synthase 4 (mycobact 6: 3027-A 2ob1-A 10.2 3.9 196 319 9 0 0 23 S TRANSFERASE leucine carboxyl methyltransferase 1 (prot 7: 3027-A 2f8l-A 10.0 3.7 182 318 8 0 0 22 S STRUCTURAL GENOMICS, UNKNOWN FUNCTION hypothetical pro 8: 3027-A 2avn-A 10.0 3.7 183 242 11 0 0 20 S STRUCTURAL GENOMICS, UNKNOWN FUNCTION ubiquinoneMENAQU 9: 3027-A 2bzg-A 9.9 3.4 182 226 13 0 0 20 S TRANSFERASE thiopurine s-methyltransferase (thiopurine 10: 3027-A 2aot-A 9.8 4.3 182 285 13 0 0 23 S TRANSFERASE histamine n-methyltransferase (hmt) (homo
Alignment with Known Proteins
1zkd is an unknown protein, and by using proteins similar to it, the functions of this unknown protein can be predicted. With 2ex4 and 1im8 showed by Dali to be the most similar, other tools are used to determine the similarity. Combinatorial Extension Method is used. Below shows the sequence alignment and structure alignment of the unknown protein with the proteins obtained from dali:
2ex4
Alignment with 2ex4 1ZKD:A 24/25 WRYXELCLGHPEHGYYV--TRDPLGREGDFTTSPEISQXFGELLGLWSASVWKAAD-EPQ 2EX4:A 24/7 IEDEKQFYS----KAKTYWKQIPPTVDGMLGGYGHISSIDINSSRKFLQRFLREGPNKTG 1ZKD:A 81/82 TLRLIEIGPGRGTXXADALRALRVLPILYQSLSVHLVEINPVLRQKQQTLLAGI-RNIHW 2EX4:A 80/64 TSCALDCGAGIGRITKRLLLPL--------FREVDMVDITEDFLVQAKTYLGEEGKRVRN 1ZKD:A 140/141 HD-----SFEDVPEGPAVILANEYFDVLPIHQAIKRETGWHERVIEIGASGELVFGVAAD 2EX4:A 132/116 YFCCGLQDFTPEPDSYDVIWIQWVIGHLT------------------------------- 1ZKD:A 195/196 PIPGFEALLPPLARLSPPGAVFEWRP--DTEILKIASRVRDQGGAALIIDYG--HLRSDV 2EX4:A 161/145 ------------------------DQHLAEFLRRCKGSL-RPNGIIVIKDNMAQE----- 1ZKD:A 251/252 GDTFQAIASHSYADPLQHPGRADLTAHV---DFDALGRAAESIGARAHGPVTQG 2EX4:A 191/175 GVILDD---------------VDSSVCRDLDVVRRIICSAG---LSLLAEERQE
Alignment Length: 294
Gaps (average per molecule): 53.5
Sequence Identity: 14.4%
RMSD min – max: 3.03A
1im8
Alignment with 1im8 1ZKD:A 59/60 QXFGELLGLWSASVWKAADEPQTLRLIEIGPGRGTXXADALRALRVLPILYQSLSVHLVE 1IM8:A 42/40 SNIITAIGXLAERFV-----TADSNVYDLGCSRGAATLSARRNI-----NQPNVKIIGID 1ZKD:A 119/120 INPVLRQKQQTLLAGI---RNIHWHD--SFEDVPEGPAVILANEYFDVLPIHQAIKRETG 1IM8:A 92/90 NSQPXVERCRQHIAAYHSEIPVEILCNDIRHVEIKNASXVILNFTLQFLP---------- 1ZKD:A 174/175 WHERVIEIGASGELVFGVAADPIPGFEALLPPLARLSPPGAVFEWRP--DTEILKIASRV 1IM8:A 142/140 ---------------------------------------------PEDRIALLTKIYEGL 1ZKD:A 232/233 RDQG--GAALIIDYG 1IM8:A 157/155 ---NPNGVLVLSEKF
Alignment Length: 195
Gaps (average per molecule): 38.5
Sequence Identity: 11%
RMSD min – max: 2.3A
Ligand and Binding Sites
Domain
InterPro Results
Pfam Results
DUF185: domain 1 of 1, from 64 to 299: score 227.1, E = 3.9e-65
*->alArwllveykllgyPYadlnlvElGaGrGtaielmsdlLryiarlv
+l++w + ++k+ ++P l+l E+G+GrGt +m+d+Lr+ r+
query 64 LLGLWSASVWKAADEP-QTLRLIEIGPGRGT---MMADALRA-LRVL 105
PdvyartryylvEiSprLaarQketLapkvaplGhdskveieatdlsglv
P +y+ ++++lvEi+p L+++Q++ La ++ ++
query 106 PILYQSLSVHLVEINPVLRQKQQTLLA-----------------GIR-NI 137
rWhdasileedPdgvptvliaNEVlDalPHDlvrfdkrgggwyErhVlvd
Whd s +e++P+g p v++aNE +D lP +++ +kr+ gw+Er V ++
query 138 HWHD-S-FEDVPEG-PAVILANEYFDVLP--IHQAIKRETGWHER-V-IE 180
ldgdfrlvysqeldplaglaltlreaaldPVKstkklvpsalskllpkll
+ ++lv+++++dp g+ ++l
query 181 IGASGELVFGVAADPIPGFEAL------------------------LPPL 206
ppaeevgygtEvYsParllellqalaerLpahrGrlLaiDYGhlaseyyh
+ +g+++E+ P e+l+++ + + +G++L+iDYGhl+s
query 207 ARLSPPGAVFEW-RPDT--EILKIASRVRD-QGGAALIIDYGHLRSD--- 249
prrksalaaemfngtllqayrqhahddpltnpssllVlyStvaqGlaDiT
g+++qa+ h + dpl +p G+aD+T
query 250 ------------VGDTFQAIASHSYADPLQHP------------GRADLT 275
ahVDFtalaradqyqtaakaagdlkvlgvet<-*
ahVDF+al +aa +g + + g+ t
query 276 AHVDFDALG------RAAESIG-ARAHGPVT 299
Domain DUF 185 has been identified by InterPro and Pfam as show above. In Pfam the E value of 3.9e-65 gives significant results showing that it is not by chance nor random that the match made was DUF185. However not much is known about DUF 185.
Function of Hypothetical Protein LOC55471 Isoform 1
ProFunc analysis reveals methyltransferase activity as the most likely biochemical function
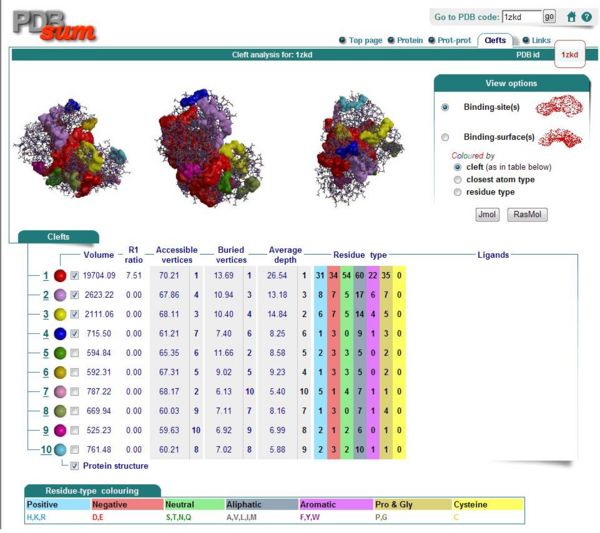
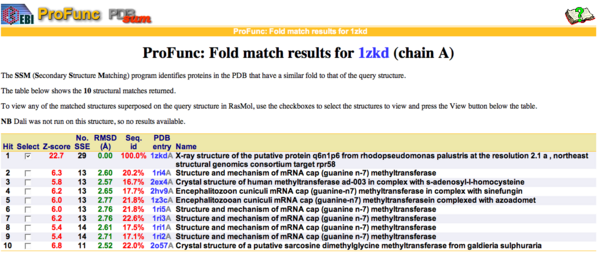
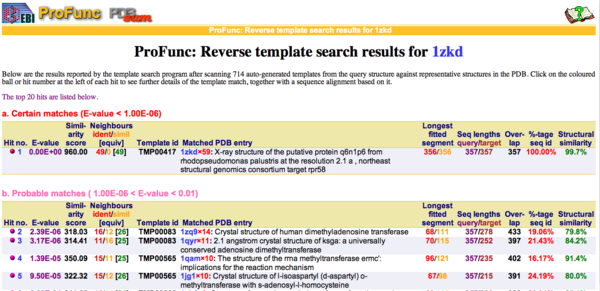
By using ProFunc (Laskowski et al, 2005) the most likely biochemical function of the unknown bacterial Protein 1zkd was determined as Methyltransferase. Matching structures were determined by SSM Secondary Structure Matching (Krissinel & Henrick, 2004) showing possible matches with 9 Methyltransferases from both human and bacteria (Fig.9).
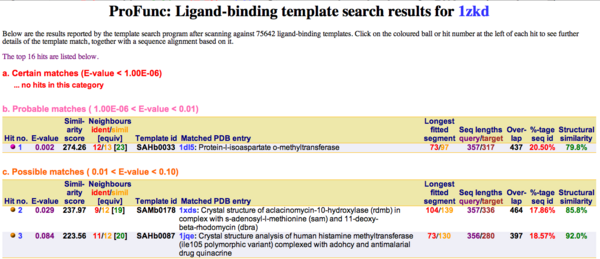
Ligand Template Matches LIG (Laskowski et al, 2005) revealed a probable match with the Protein-l-isoaspartate o-methyltransferase 1dl5 (Fig.10).
REV Reverse Template Matches (Laskowski et al, 2005) also showed probable matches for several methyltransferases (Fig.11).
Superfamily program searches against a library of Hidden Markov Models HMMs (Gough et al, 2001; Madera et al, 2004) derived from SCOP families revealed similarities to the superfamily S-Adenosylmethionine-dependent Methyltransferases (E-value 6.69e-06). No DNA binding motifs (helix-turn-helix) were found in the ProFunc search.
Genomic context of the 1izkd gene
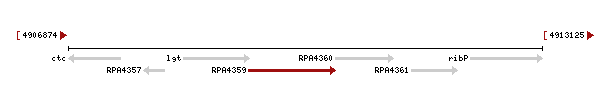
Genomic context of 1zkd in the genome of Rhodopseudomonas palustris from the NCBI Entrez Gene database shows a genomic co-localisation with another transferase, an oxidase, a kinase and another hypothetical protein (Fig.12).
Localisation of 1zkd orthologs in the cell
Nucleo (Nuclear Protein Localisation Prediction) predicted a chance of 0.07 for the mouse ortholog and a chance of 0.20 for the human ortholog of 1zkd to be located in the nucleus (Hawkins et al, 2006).
LOCATE data was available for the mouse ortholog showing that it is a soluble, non-secreted protein with higher scores for a localisation in mitochondria or the cytoplasm (Fink et al, 2006).
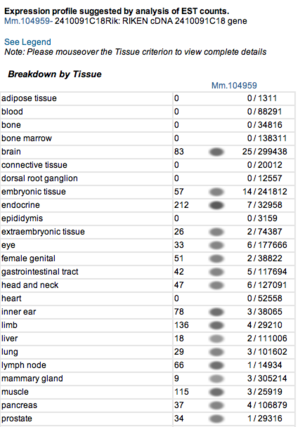
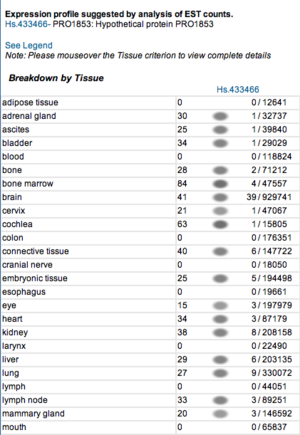
Expression profiles of mouse and human orthologs
Expression profile data of the mouse and human ortholog were suggested by analysis of EST counts from NCBI UniGene database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=unigene). ESTs were found in diverse tissues including brain, liver, lung, muscle and endocrine system showing that the target protein is expressed in a wide range of different cells (Fig.13a,b).
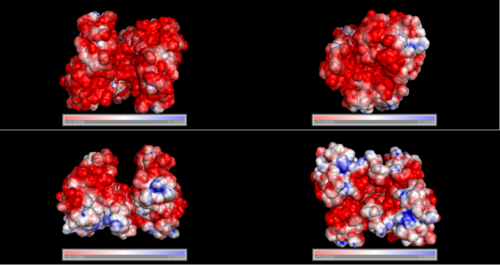
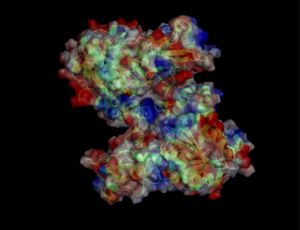
Electrostatic properties of the 1zkd protein surface
Electrostatic properties and surface charges of 1zkd were modelled using Adaptive Poisson-Boltzmann Solver APBS (Baker et al, 2001) and visualisation was performed by using Pymol (http://www.pymol.org). According to the resulting model, the 1zkd protein got a mostly negatively charged surface (Fig.14a,b), indicating that interactions with the negatively charged backbone of nucleic acids are rather unlikely.
Evolution of Hypothetical Protein LOC55471 Isoform 1
BLAST P
BLASTP results produced 47 multiple aligned sequences to the bacterial sequence of the 1ZKD protein. The results are as follow BLASTP results.
The highlighted sequences show the 1ZKD protein sequence data and the closest match or best aligned sequence (>gi|39937419|ref|NP_949695.1| DUF185 [Rhodopseudomonas palustris CGA009]).
Clustal X
The following are some ClustalX images that were produced.
After running Clustal X many sequences were omitted as they created many gaps in the MSA multiple sequence alignment. In the process, all of the mouse and human comparative sequences were also omitted and this is visible in the evolutionary tree constructed at the end.
This however allowed the focus of the research into the evolutionary construct of the 1ZKD protein to be more specific in relation to other bacteria’s.
After carefully analyzing the MSA in a clustal X format, the closest available sequence to the protein sequence of 1ZKD was the DUF185 protein sequence from Rhodopseudomonas palustris bacteria. The only differences were the occurrence of eight different amino acids randomly in the sequence and the eight extra amino acids at the '3’' or the 'C-terminus' end of the 1ZKD amino acid sequence.
Our protein amino acid sequence is no. 32 and the closest matched sequence is of DUF185 amino acid sequence is at no. 31.
Protdist
Protdist results and how it looks like.
The number at the top of the page indicates the number of sequences uploaded.
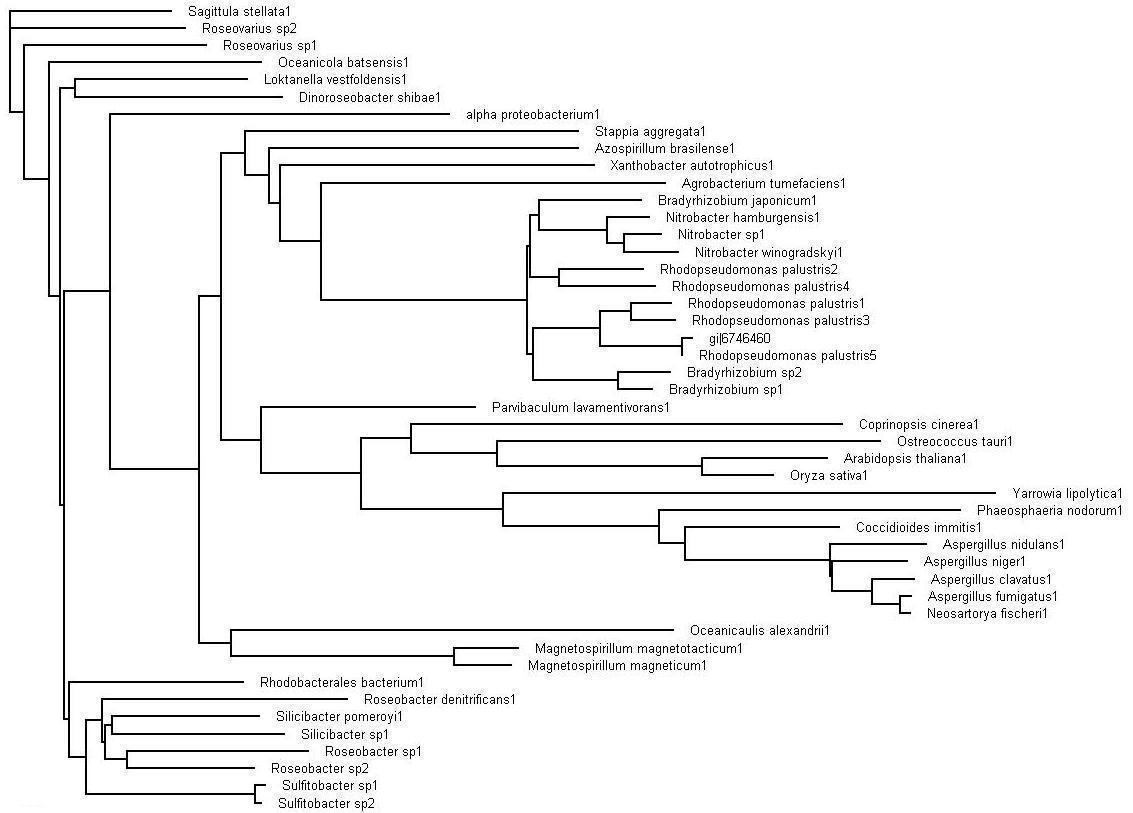
Bootstrap values for Bacterial Protein
The evolutionary tree obtained after bootstrapping. This view of the tree via the Treeview program allows for the analyzing of the the organisms that are in close sequence proximity as our sequence.
Evolutionary Tree
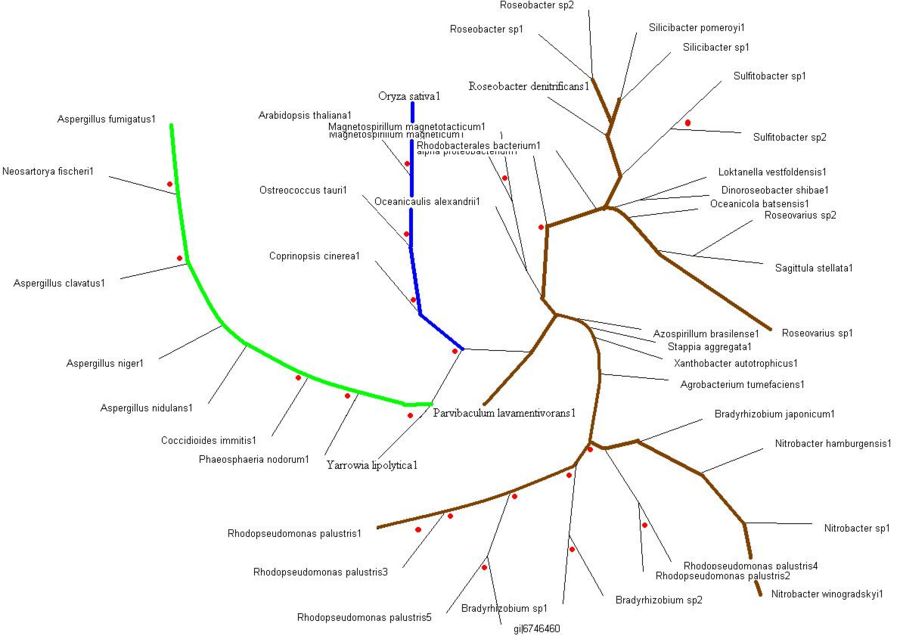
>>> Brown colored branches consists of organisms from a Bacterial lineage, and most of them happen to be gram-negative bacteria. Most of the bacteria’s in the branches seem to be from the alpha proteobacteria family. Some of bacteria also show similarities in their ability for nitrogen fixation namely Rhodopseudomonas palustris, Bradyrhizobium japonicum, Agrobacterium tumefaciens and Azospirillum brasilense.
>>> Green colored branches consist of organisms from the Fungi kingdom, mostly found growing in the soil.
>>> Blue colored branches consist of organisms from the Plantae kingdom, some showing affinity to being associated with yeast.
>>> Red dots denote branches/lineages with bootstrap values of more than 75%, which signifies very high confidence on the branching of the organisms in the tree.
Return to Report on 1zkd