2i2O Protein Evolution Presentation
From MDWiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
- Evolution of eIF4G occurred early on in euks
- Evolution of three domains within eIF4G - MIF4G being one of them
- Research indicates all three domains present in early euks
- Possible loss of these domains within other organisms
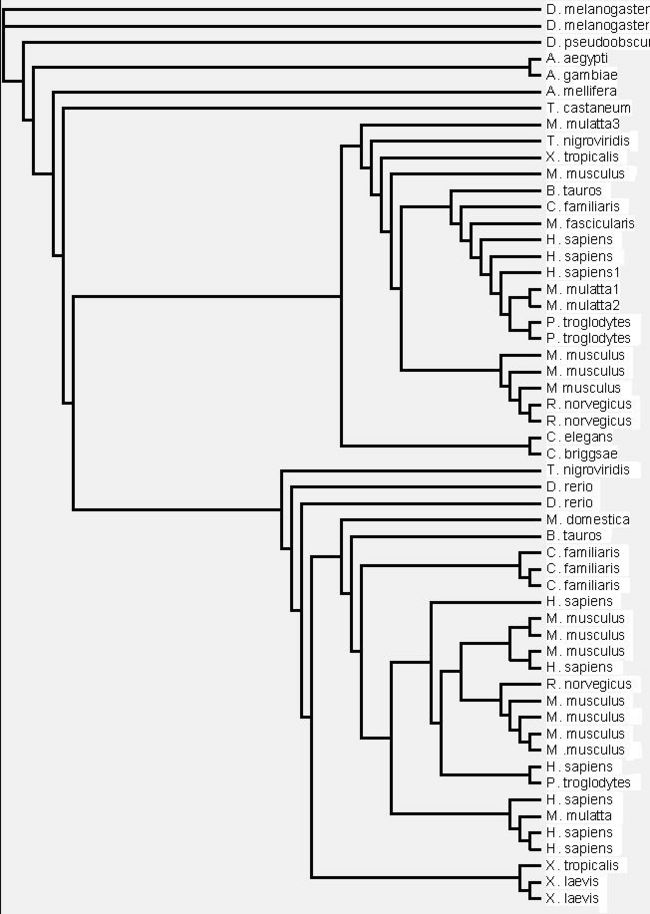
- Three programs used to construct phylogenetic tree
- Blast used to find significant sequences
- 54 sequences chosen because E-value under 0.01
Figure 1.0 Protein sequence of MIF4G domain containing protein found in Homo sapiens.
- ClustalX used
- Multiple alignment of the 55 sequences undertaken
- First draft phylogenetic tree created
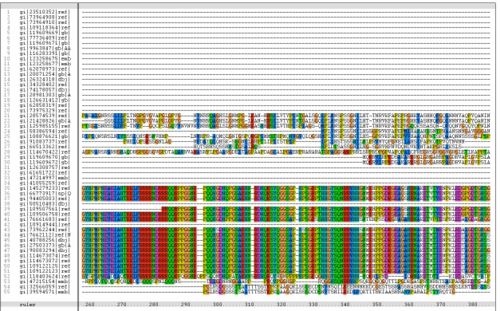
Figure 1.1 Multiple alignment sequence of the MIF4G domain containing protein. The top sequence is the human sequence of the MIF4G protein and the focus of this report.
- Final phylogenetic tree constructed by using program Phylip
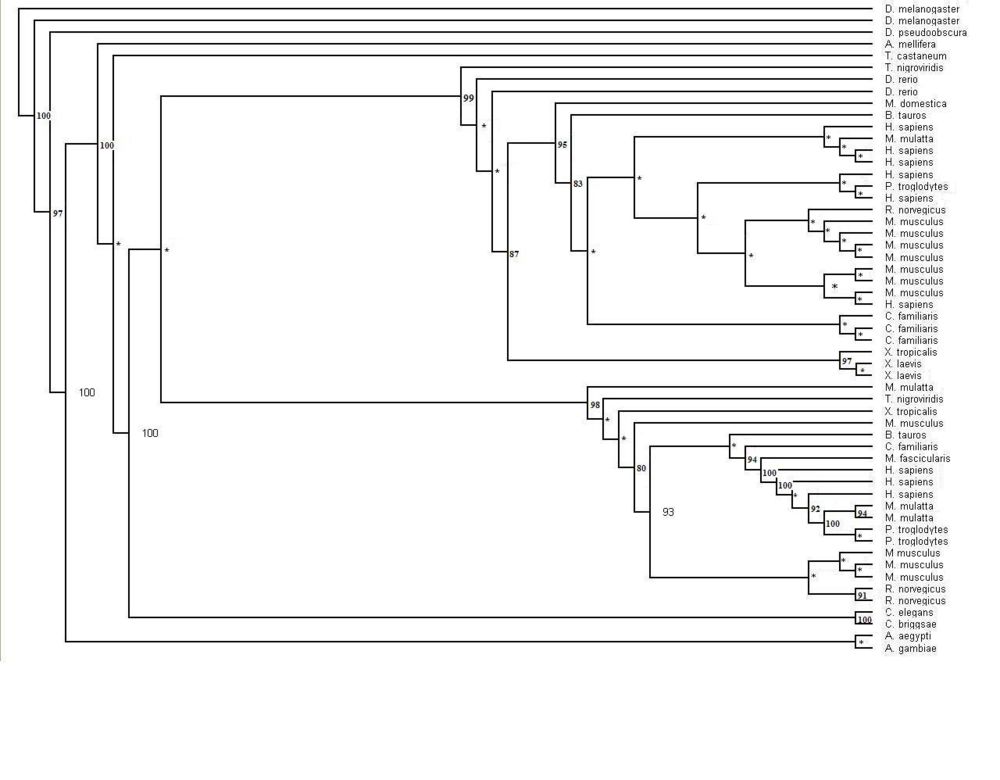
Figure 1.1 Phylogenetic tree of the 55 significant sequences closest to MIFG4 protein. Bootstrapping values shown on the tree. * denotes a bootstrap value less than 75
- No sequences found represented the two other euk. families, plants and fungi
- Goes against other evidence that suggests all 3 eIF4G domains present in early euks
- Possible reasons include e-value cut-offs, sequences dissimilar to human protein and deletion of the protein domain from these eukaryotes
- Bootstrapped tree interesting that split into two smaller trees consisting of the vertebrates.
- Divergence of the ancestral MIF4G protein in Metazoans
- Need to perform different functions in different types of cells
- More info needed on the other MIF4G proteins from the other species to also determine their structure and function