2i2O Protein Function Presentation
Function Presentation:
The MIF4G domain containing protein is the middle protein in the eukaryotic initiation factor 4G. A study of the literature showed that eIF4G and in particular the middle domain was important in the creation of a molecular bridge between eIF4G, eIF4A and RNA ribosomal units. However the actual function of MIF4G was still undiscovered. It was my task to Identify some more information regarding the proteins function and properties. For the most part this was done using computational tools and databases such as ProFunc, ProKnow, LOCATE, PDB, Pfam and many others.
Unfortunately our protein hasn’t been entered into many databases and most of the searches performed returned few or no results. To overcome this obstacle I decided to do a comparative study. I identified the closest related protein so far known to MIF4G, the MIF4G-like protein discovered in the zebra fish. Much more information about this protein was available including structural and evolutionary analysis. This assumption was made based on structural and functional comparisons between the two proteins as well as thorough literature searches.
My methods were to search a database with the protein name (MIF4G or 2i2O), FASTA sequence or accession number for the original protein. In cases where results were lacking or not significant I performed a second search using MIF4G-like protein or 1hu3 (or FASTA sequences etc). Significant results from both proteins were compared for similarity. This tool also allowed me to fill the gaps in the available information enough to make possible projections, hypotheses and inferences.
Searching LOCATE with the protein name MIF4G showed that the most probable location (0.93 probability) of the protein was the cytoplasm of cells was soluble and non-secreted and also a polyadenylate binding protein-interacting protein. Furthermore, the top three of these proteins were identified as Riken cDNA templates, being similar to the location and possible function of MIF4G, all containing an ARM repeat.
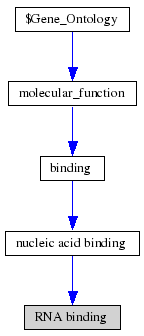
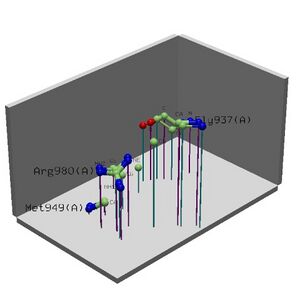
ProKnow: Identified that the likely function of MIF4G 2i2OA was RNA binding See Figure 2.4.
In parallel to the Superfamily HMM program (Gough et al, 2001), LOCATE showed the protein to contain ARM repeats (armadillo repeats). ARM and HEAT repeats are repeats approximately 50 residues long tandemly repeated throughout many eukaryotic proteins. The function of which is largely unknown except to say both repeats have been implicated as participating in the regulation of protein-protein interactions.
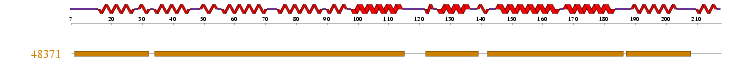
1 motif match was found to the Superfamily HMM library at residues 8-31, 34-114, 122-138, 142-185, 187-207 in the ARM repeat superfamily.
Figure 2.3: Superfamily analysis revealed 1 sequence motif in the sequence.
Originally it was believed that ARM and HEAT repeats were similar however it was recently found that the two repeats were divergent and contain significant structural and functional differences. Namely the ARM repeat consists of two helices and the HEAT domain of three. This is consistent with our findings, that the domain is rich in alpha helices and is significant to our domain containing protein MIF4G as it provides further evidence to the function of MIF4G being the mediation of protein-protein interactions during the initiation of translation.
The query submitted to Pfam using MIF4G domain identified the domain to be occurring in the eukaryotic translation initiation factor IV (eIF4) as well as in NMD2p and CBP80 (nonsense mediated mRNA decay protein 2 and nuclear cap-binding protein respectively). Literature showed the proteins to be structurally similar to MIF4G and also as to domains from within eIF4 domain known as HEAT domains. HEAT domain are a superhelical forming scaffolding matrice that is comprised of single HEAT repeat units made up of a pair of anti-parallel helices linked by a flexible loop. These can also occur in series. Three consecutive HEAT domains are present within eIF4 of which MIF4G is congruent with HEAT-1. CBP80 contains three HEAT domains and is structurally similar to eIF4G. Its middle domain has been proposed to be similar to MIF4G.
The NEST analysis produced 3 functionally significant and conserved hits. We can infer that these structural motifs are important sites for the function of the protein however further analysis is required before a more specific conclusion can be made as to the significance of identified NESTS and there functional properties. Combining the information gathered about the function and functional sites we can hypothesise that the structural motifs identified by NEST are important for RNA binding.
Table 2.1 NEST Results
Ramachandran Solvent
Nest Score Residue range Residue region accessibility Cleft Depth cleft Res.conserv
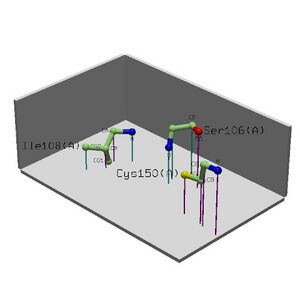
1. 4.96 Tyr9(A)-Ile11(A) Tyr9(A) RIGHT 3.38% - - 1.00
Lys10(A) LEFT 0.52% - - 1.00
Ile11(A) - 0.31% - - 0.88
2. 3.46 Gly204(A)-Trp206(A) Gly204(A) RIGHT 0.00% - - 0.60
Gly205(A) LEFT 0.98% 2 6.70 1.00
Trp206(A) LEFT 0.00% - - 0.77
3. 2.28 Thr70(A)-Gly72(A) Thr70(A) RIGHT 0.00% - - 0.62
Asn71(A) LEFT 1.21% - - 0.68
Gly72(A) - 0.00% 4 4.42 0.54
Figure 2.6 Alignment of 2i2O generated by ProFunc
Cleft Analysis found four highly conserved and hydrophobic regions. These results show potential binding sites on the protein and their possible residues. The residue type provides clues as to the type of molecule that binds to the functional site and hence what the function of the protein is. Looking collaboratively with the results from LOCATE and ProKnow further show the function to be RNA binding during the initiation of translation phase. Unfortunately without experimental analysis there is no way of knowing exactly which residues are important for function and thus the exact function of the protein. Moreover, backing this up is literature that suggests MIF4G binds to eIF4A, an RNA helicase and RNA and is speculated to play a role in the binding of eIF4A to RNA.
Table 2.2 Cleft Analysis Results
Region R1 Accessible Buried Average Residue Residue Gap Volume 1 Ratio Vertices Vertices Depth Type Conservation Ligands 1 822.66 0.67 66.51% 2 10.40% 3 11.19 1 23662.. 1....223..2 2 1232.30 - 65.69% 3 10.80% 1 10.31 3 564644. ...1154558 3 1160.58 - 66.75% 1 8.98% 8 10.95 2 464552. ...1143548 4 931.50 - 59.62% 6 9.06% 7 8.73 5 225421. .....12257 5 827.72 - 57.62% 8 9.51% 6 8.58 6 34631.. .....22337 6 885.94 - 61.42% 4 10.04% 4 8.27 7 215421. .....12266 7 910.83 - 60.12% 5 7.92% 9 7.52 10 34263.1 ...1.11665 8 772.45 - 58.35% 7 9.64% 5 8.88 4 533.2.. ....114313 9 682.17 - 55.10% 10 5.75% 10 7.63 9 323112. .....14351 NI 502(1 atom) 10 585.14 - 57.04% 9 10.45% 2 7.93 8 2132.1. .....1317. NI 501(1 atom)
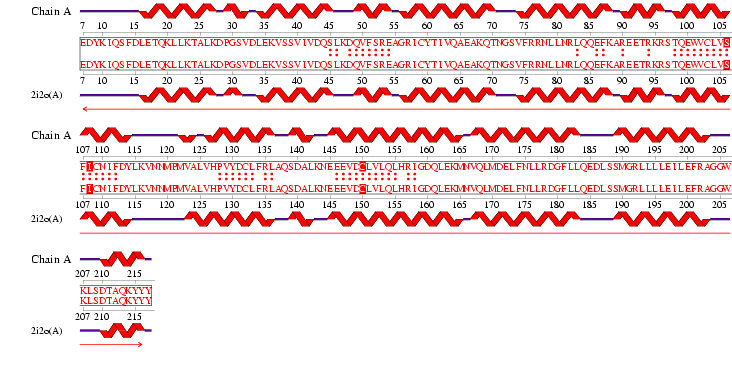
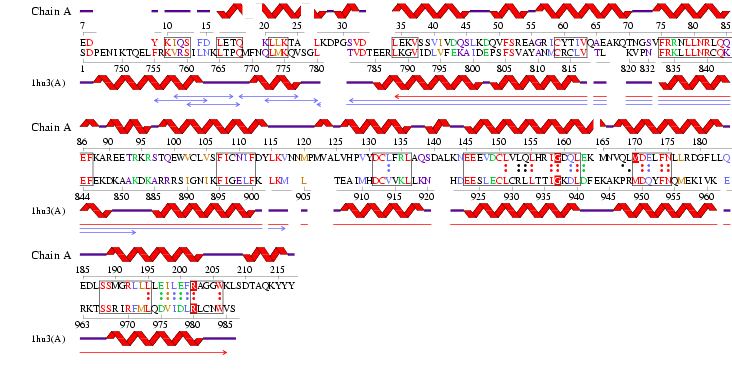
See Figure 2.7 Generated by structure comparison in PDB vs. RNA template of 1hu3 to 2i2O
The results for 3D functional template demonstrate that the Reverse template comparison versus PDB structures of 1hu3 and 2i2O show they are significantly both structurally and functionally similar. The figure produced (Figure 2.5) shows that all of the regions of high sequence identity (boxed sequence) correspond to structurally fittbale regions (as denoted by the red and blue arrows). This segment also contains three matched template side chains and several residues that are equivalenced from within 10Å of the template residues (red boxed letters and dots between letters). Therefore it is possible to assume that the identified regions could be conserved functional regions common to both proteins.
Figure 2.9 RNA Template alignment 1hu3 vs 2i2O.
In Conclusion based on computational analysis it can be predicted that the likely function of MIF4G domain containing protein is to bind RNA in such a way that facilitates the simultaneous binding of another eIF4 domain eIF4A and small ribosomal units. It is expected that the function of this will allow the initiation of translation within eukaryotic cells. HEAT-domains and ARM repeats although their function is also relatively unknown are likely to play a pivotal role in the operation of MIF4G. These hypotheses have been made on the assumptions that the differences between 2i2O and 1hu3 structurally and functionally are negligible.
Return to Presentation