3b5q Function: Difference between revisions
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
'''N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase''' cleaves the 6-sulfate groups of N-acetyl-D-galactosamine 6-sulfate units in chondroitin sulfate and D-galactose 6-sulfate units in keratan sulfate.'''N-sulphoglucosamine sulphohydrolase''' is also known as heparine sulfamidase, which catalyses the hydrolysis of Sulfur-Nitrogen bonds. N-sulphoglucosamine sulphohydrolase is rsponsible for the degradation of glucosaminlglycan and glycan structure of extra cellular matrix. | '''N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase''' cleaves the 6-sulfate groups of N-acetyl-D-galactosamine 6-sulfate units in chondroitin sulfate and D-galactose 6-sulfate units in keratan sulfate.'''N-sulphoglucosamine sulphohydrolase''' is also known as heparine sulfamidase, which catalyses the hydrolysis of Sulfur-Nitrogen bonds. N-sulphoglucosamine sulphohydrolase is rsponsible for the degradation of glucosaminlglycan and glycan structure of extra cellular matrix. | ||
:N-sulfo-D-glucosamine + H<sub>2</sub>O <math>\rightleftharpoons</math> D-glucosamine + sulfate | |||
Revision as of 04:00, 21 May 2008
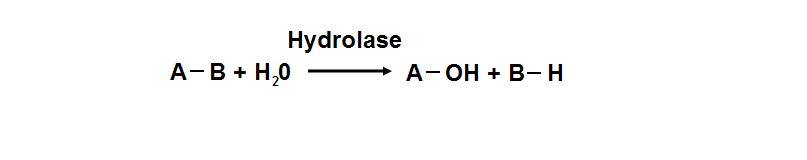
Protein data base profile characteris arylsulfatase asa hydrolase and a sulfatase. A hydrolase is an enzyme which hydrolyses a chemical bond. The general reaction can be shown as follows.
Group of hydrolaes are named as EC 3 in enzyme classification.
1. Function of sulfatases
Sulfatases are enzymes,which hydrolyse sulfate ester bonds of substrates. These are categorised as EC 3.1.6. in enzyme classifications. Most of the family members has shown to contain a highly conserved cystine residue and a bivalent metal binding site.
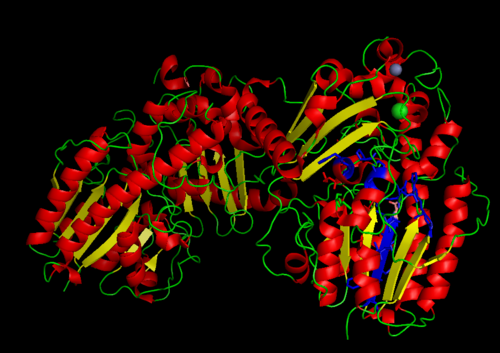
2. Functional site
MSA data revealed some conserved residues on the sequence. They were mapped on the three dimantional structure.
Highly conserved regions of the protein revealed in MSA are highlighted in blue, while ligands; Zn and Cl; are shown in green and grey respectively. However region of high conservation seems to be physically further from ligand binding sites. May be sudgessting that ligands only play a role in stabilizing the protein conformation, hense the active site; for the enzyme to perfprm its catalytic functions.
. . . .
.. . . . .
..
..
. . . . . . ..
. . . .
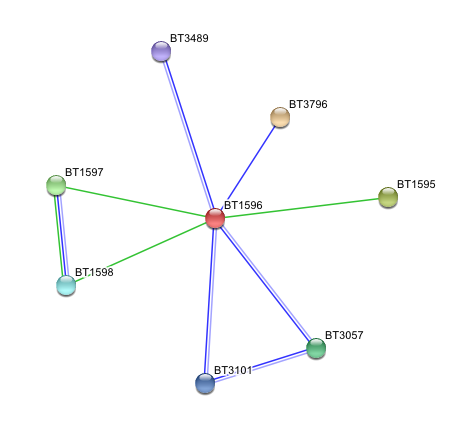
3. Arylsulfatase K (BT1596) Interactions with other proteins
Input Protein
- BT1596 Putative sulfatase yidJ (481 aa) of Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron.
Predicted Functional Partners
- BT3796: Putative secreted sulfatase ydeN (518 aa).
- BT1595 Transcription termination factor rho (722 aa).
- BT1597 Two-component system sensor histidine kinase (539 aa).
- BT3057 N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase (508 aa).
- BT1598 Putative two-component system sensor histidine (655 aa).
- BT3101 N-sulphoglucosamine sulphohydrolase (455 aa).
- BT3489 Arylsulfatase B {UniProtKB/TrEMBL-Q8A219} (458 aa).
N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase cleaves the 6-sulfate groups of N-acetyl-D-galactosamine 6-sulfate units in chondroitin sulfate and D-galactose 6-sulfate units in keratan sulfate.N-sulphoglucosamine sulphohydrolase is also known as heparine sulfamidase, which catalyses the hydrolysis of Sulfur-Nitrogen bonds. N-sulphoglucosamine sulphohydrolase is rsponsible for the degradation of glucosaminlglycan and glycan structure of extra cellular matrix.
- N-sulfo-D-glucosamine + H2O <math>\rightleftharpoons</math> D-glucosamine + sulfate
Click here to go Back