ATP binding domain 4 Functions
My sequences:Putative n-type ATP pyrophosphatase from Pyrococcus furiosus, the Northeast Structural Genomics Target PfR23
Adenine nucleotide alpha hydrolases, AANH_like (cl00292), superfamily includes members of N type ATP PPases, ATP sulphurylases Universal Stress Response protein and electron transfer flavoprotein (ETF). The domain forms a apha/beta/apha fold which binds to Adenosine nucleotide. Our sequence of interest is a putative n-type ATP pyrophosphatase that are under AAHN-like superfamily.
Pfam from Sanger suggests that N-type ATP Pyrophosphatase belongs to a family named ATP-binding 4 (PF01902), which contains a 200 amino acids long strongly conserved motif of SGGKD near the N-terminus.
The family ATP-binding 4 is a member of clan PP-loop (CL0039), which is comprised of 9 members: Arginossucinate synthase, Asn synthase, ATP binding 3, Exs B, NAD synthase, PAPS reductase, Thianmine biosynthesis protein, tRNA Methyl transferase and finally where our sequence belongs to -- ATP binding 4.
Although our protein sequence shows little homology with human ATP Binding domain 4 proteins, having % sequence ID = 36.8%, understanding the function of human ATPPD4 can help us infer functions of our sequence.
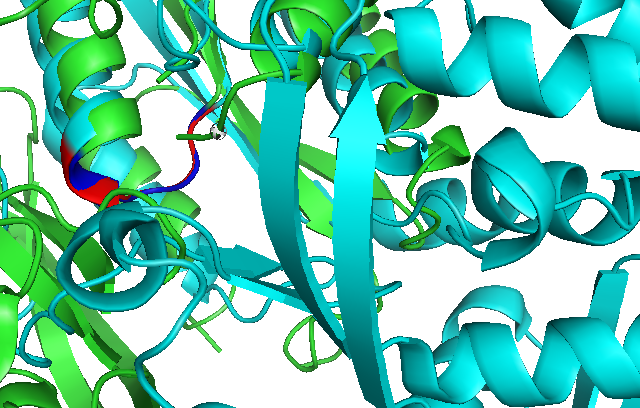
Use of Dali reveals similar domain alignment of our sequence with Argininosuccinate Synthase (2nz2-A), which Z-score is 11.0% (indicatively significant domain similarity). Therefore, we use Pymol to align conserved residues of 1RU8 and 2NZ2 (align 1RU8 & i. 11-16, 2NZ2 & i. 11-15). Close structure resemblance is a strong indication of function resemblance.
- ATP pyrophosphatase (ATP PPase) is used to assist lysidine formation using a lysine-specific loop and tRNA recognition domain
- Lysidine is a lysine-combined modified cytidine, locating at antcodon wobble position (34) of bacterial tRNA
- Usually ATP-pyrophosphatatse has a domain of GMP synthetase, for adding adenine and help lysine attack on Carbon atom.
http://www.pnas.org/content/102/21/7487.abstract
--
- NAD+ synthetase belongs to a member of the family of N-type ATP pyrophosphatase (ATP PPases)
- Some other members of N-type ATP pyrophosphatase include NAD+ synthetase, GMP synthetase, asparagine synthetase and argininosuccinate synthetase
- this family is characterised by strictly conserved fingerprint sequence Ser-Gly-Gly-X-Ser/ Thr-Ser/ Thr at P-loop (this is found by the comparison of 3-D structures of NAD+ synthetase and GMP synthetase
- Since they are in the same family, we can infer their structure similarities and propose the functions of our sequences. - Look for the ATP-binding sites on ref[11]
- Rizzi, M., et al., & Galizzi, A. (1996). Crystal structure of NH3-dependent NAD synthetase from Bacillus subtilis. EMBO J. 15, 5125-5134
--
- ([A/S]-[F/y]-S-G-G-[L/V]-D-T-[S/T] is a common consensus sequences that contains a glycine-rich motif that is common to a subset of ATP pyrophosphatases, which is known as 'N-type' ATP pyrophosphatases.
- N-type ATP pyrophosphatases all catalyses a substrate adenylation to activate a carbonyl C=O or carboxyl COO- group for the subsequent attack of a nitrogen nucleopile.
- This glycine-rich motif will form a modified P loop within the nucleotide binding domain, known as 'PP-motif'.
- Lemke, C, T. and Howell, P.L. 2001, The 1.6A Crystal Structure of E.coli Argininosuccinate Synthetase Suggests a Confomational Change during Catalysis, Structure 9:1153-1164.
--
Gough, J., Karplus, K., Hughey, R. and Chothia, C. (2001). "Assignment of Homology to Genome Sequences using a Library of Hidden Markov Models that Represent all Proteins of Known Structure." J. Mol. Biol., 313(4), 903-919.