Arylformamidase Function
Lines of evidence:
Sequence
Structural evidence
Genomic Context
Cellular Context (location)
Species Similarities
Literature Evidence
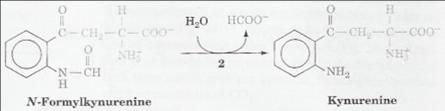
Return to the main page... Arylformamidase – Functional Analysis Possible ExPASy entry: 3.5.1.9 Deducing Function pdb|2PBL|A Chain A, Crystal Structure Of Putative Thioesterase (... 516 e-145 reference ref|YP_614486.1| putative esterase/lipase/thioesterase [Siliciba... 514 e-144 reference ref|ZP_01753905.1| possible esterase/lipase/thioesterase [Roseob... 416 e-114 prokaryotic genome pipeline ref|ZP_02144596.1| putative esterase/lipase/thioesterase [Phaeob... 409 e-112 prokaryotic genome pipeline ref|ZP_02147804.1| possible esterase/lipase/thioesterase [Phaeob... 408 e-112 prokaryotic genome pipeline ref|ZP_01055720.1| possible esterase/lipase/thioesterase [Roseob... 396 e-109 prokaryotic genome pipeline ref|ZP_01441538.1| possible esterase/lipase/thioesterase [Roseov... 318 3e-085 prokaryotic genome pipeline Initially, an examination of the closest results (E-value < 10e-70) provided no clues towards the protein’s function. The majority of the results were the outcome of the NCBI Prokaryotic Genomes Automatic Annotation Pipeline Group. The automatic annotations returned suggested the sequence represented a putative esterase, lipase or thioesterase. Reason… No functional data or useful associated literature was returned. A search of PubMed using common terms namely appearing in the annotation of the blast results ‘arylformamidase’ and ‘kynurenine formamidase’ returned some useful literature. Literature Notes 2005 Pabarcus Sequence used accession number - NP_082103.1. E-value from BLAST - 6e-017. • Function: o Catalyzes the hydrolysis of N-formyl-L-kynurenine (NFK) to L-kynurenine. The second step in the pathway for conversion of tryptophan to nicotinic acid, NAD(H) and NADP(H). o Assayed through activity for hydrolyzing NFK. o Current interest in considering organophosphate toxicology. o Inactivation in mice results in a profound imbalance of metabolites of the kynurenine pathway of tryptophan degradation, which may explain the kidney deterioration and abnormal immune system.
Structure: o An α/β-hydrolase fold is suggested for AFMID based onits primary sequence and predicted secondary structure. o A three-dimensional model based on the structures of homologous proteins implicates Ser162, Asp247, and His279 as the active site triad. Site-directed mutagenesis of catalytic triad residues.
Sequence: o AFMID has been characterized at the nucleotide and/or protein level in Wve species; Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Polaribacter Wlamentus, Gemmata sp. Wal-1, Drosophila melanogaster, and Mususculus with six protein and ten nucleotide sequences found for AFMID using the National Center for Biotechnology Information Entrez search engine.
2005 Casida
• Secondary target conferring toxicity in hen eggs of organophosphorous (OP)-based compounds.
2005 Dobrovolsky
• Afmid knockout experiment. • Afmid/Tk -deficient mice are known to develop sclerosis of glomeruli and to have an abnormal immune system. • 13% residual formyl-kynurenine hydrolysis in the kidney of KO mice, suggesting the existence of a formamidase other than Afmid.