Arylformamidase Sequence & Homology: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Method == | == Method == | ||
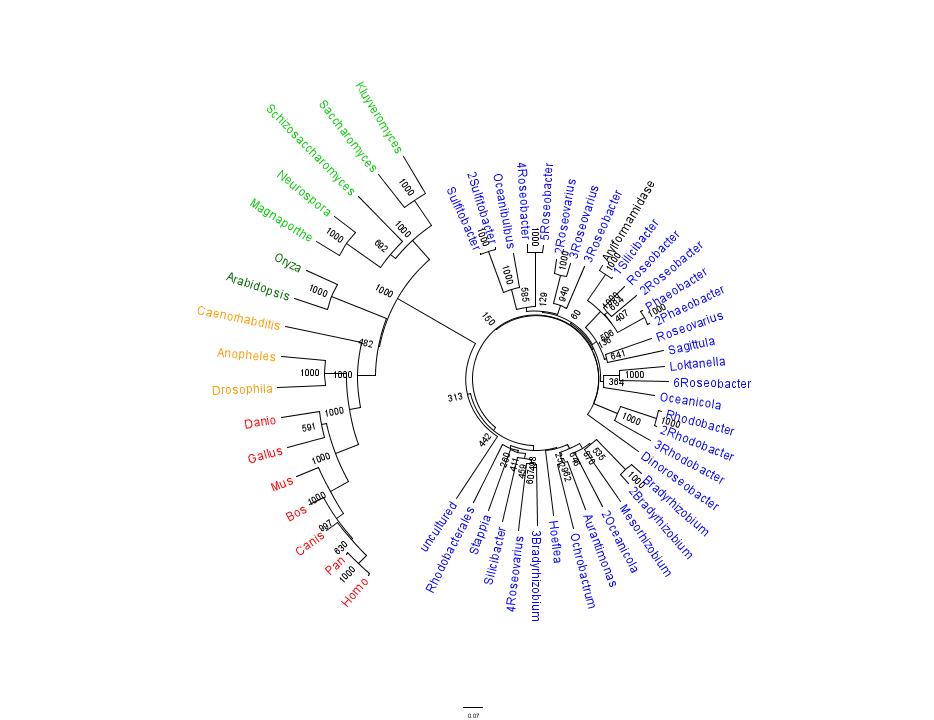
A BLAST search was performed on the bacterial sequence of Arylformamidase. The top scoring matches to an E-value of 3e-054, 35 sequences in total, were selected. Eukaryotic homologous sequences sequences were found using HOMOLOGENE. These included vertebrates, invertebrates, plants and single-celled eukaryotes. These were appended to the list and a multple sequece alignment was performed using CLUSTAL X. The alignment revealed several conserved regions accross all species, thereby indicating a high level of conservation from Bacteria through Eukaryota. | A BLAST search was performed on the bacterial sequence of Arylformamidase. The top scoring matches to an E-value of 3e-054, 35 sequences in total, were selected. Eukaryotic homologous sequences sequences were found using HOMOLOGENE. These included vertebrates, invertebrates, plants and single-celled eukaryotes. These were appended to the list and a multple sequece alignment was performed using CLUSTAL X. The alignment revealed several conserved regions accross all species, thereby indicating a high level of conservation from Bacteria through Eukaryota. | ||
The data output from the multiple sequence alignment was bootstrapped 100 times and a phylogenetic tree was created using the neighbour-joining method. The program FigTree was used to create the visual representation of this tree. | |||
This gave the following tree: | This gave the following tree: | ||
[[Image: | [[Image:NewBOOTtree2.png]] | ||
Unrooted phylogenetic tree | |||
Unrooted phylogenetic tree of highest scoring results from a BLAST search of bacterial sequnces using a non-redundant database and homologous eukaryotic sequences sourced from HOMOLOGENE: | |||
Revision as of 07:19, 28 May 2008
Method
A BLAST search was performed on the bacterial sequence of Arylformamidase. The top scoring matches to an E-value of 3e-054, 35 sequences in total, were selected. Eukaryotic homologous sequences sequences were found using HOMOLOGENE. These included vertebrates, invertebrates, plants and single-celled eukaryotes. These were appended to the list and a multple sequece alignment was performed using CLUSTAL X. The alignment revealed several conserved regions accross all species, thereby indicating a high level of conservation from Bacteria through Eukaryota.
The data output from the multiple sequence alignment was bootstrapped 100 times and a phylogenetic tree was created using the neighbour-joining method. The program FigTree was used to create the visual representation of this tree.
This gave the following tree:
Unrooted phylogenetic tree of highest scoring results from a BLAST search of bacterial sequnces using a non-redundant database and homologous eukaryotic sequences sourced from HOMOLOGENE: