Evolution: Difference between revisions
JasonCheong (talk | contribs) |
JasonCheong (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
=='''Query Sequences (2gfh)'''== | =='''Query Sequences (2gfh)'''== | ||
The following query protein sequence of N-acetylneuraminic Acid was obtained from GenBank: | |||
{| border="1" cellpadding="15" cellspacing="0" | {| border="1" cellpadding="15" cellspacing="0" | ||
| Line 15: | Line 17: | ||
'''svlelpallq sidckvsmsv''' | '''svlelpallq sidckvsmsv''' | ||
|} | |} | ||
From the BlastP similarity sequence search, a total of 500 proteins were yielded. | |||
Only a total of 38 proteins were used for comparison as these had shown higher homology to the query sequence, in contrast with the remainder of the search results. | |||
These proteins were chosen according to their bit scores and E-values. Two more outlier partial sequences contributing to poor overall alignment (huge deletion gaps) were subsequently removed. The remaining 36 sequences were used for the generation of the phylogenetic tree (and bootstrapped tree as well). | |||
'''Figure 1.''' '''Amino Acid Sequence (260 aa)''' of N-acetylneuraminic Acid (2gfh) protein from ''Mus musculus'' (House Mouse) | '''Figure 1.''' '''Amino Acid Sequence (260 aa)''' of N-acetylneuraminic Acid (2gfh) protein from ''Mus musculus'' (House Mouse) | ||
Revision as of 17:26, 10 June 2007
Query Sequences (2gfh)
The following query protein sequence of N-acetylneuraminic Acid was obtained from GenBank:
| mgsdkihhhh hhmglsrvra vffdldntli dtagasrrgm levikllqsk yhykeeaeii
cdkvqvklsk ecfhpystci tdvrtshwee aiqetkggad nrklaeecyf lwkstrlqhm iladdvkaml telrkevrll lltngdrqtq rekieacacq syfdaivigg eqkeekpaps ifyhccdllg vqpgdcvmvg dtletdiqgg lnaglkatvw inksgrvplt sspmphymvs svlelpallq sidckvsmsv |
From the BlastP similarity sequence search, a total of 500 proteins were yielded.
Only a total of 38 proteins were used for comparison as these had shown higher homology to the query sequence, in contrast with the remainder of the search results.
These proteins were chosen according to their bit scores and E-values. Two more outlier partial sequences contributing to poor overall alignment (huge deletion gaps) were subsequently removed. The remaining 36 sequences were used for the generation of the phylogenetic tree (and bootstrapped tree as well).
Figure 1. Amino Acid Sequence (260 aa) of N-acetylneuraminic Acid (2gfh) protein from Mus musculus (House Mouse)
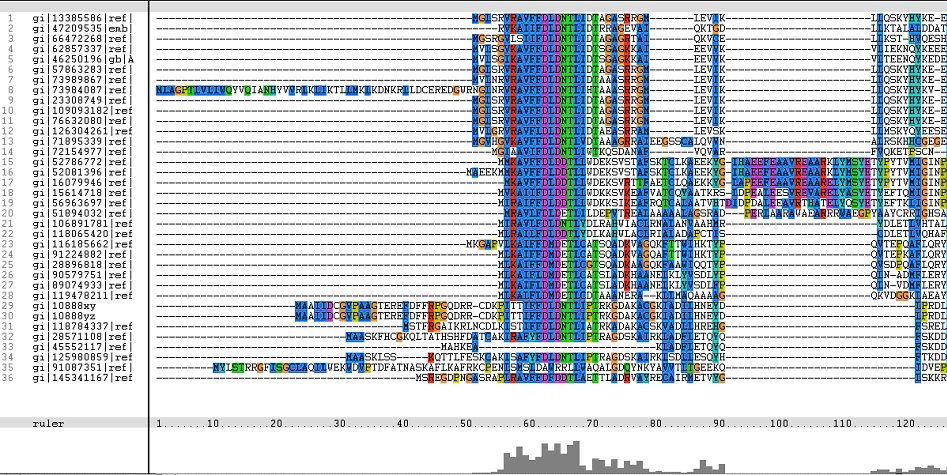
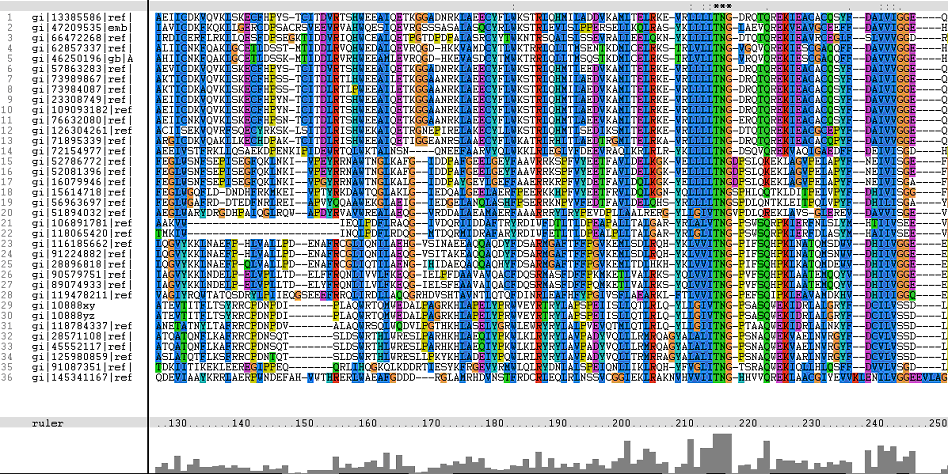
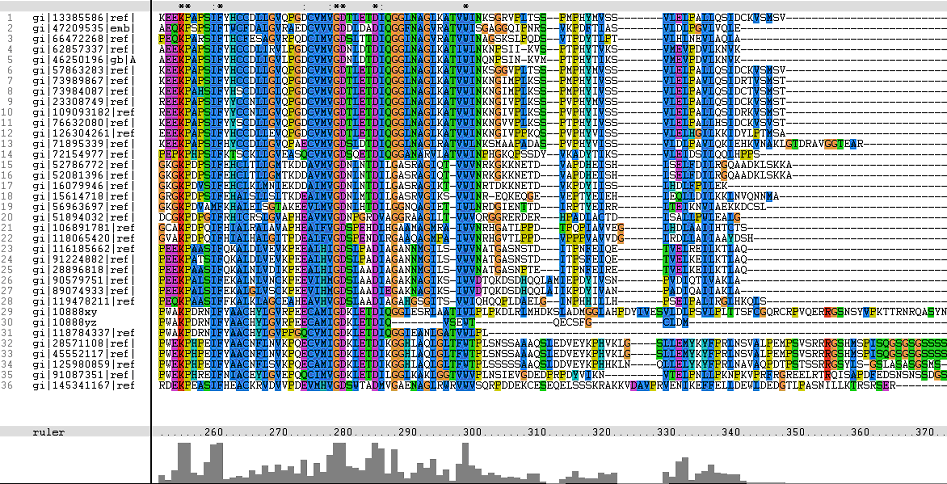
Multiple Sequence Alignments (msa)
Figure 1. Multiple Sequence Alignments of 2gfh amino acid sequences with that of other similar protein sequences in various organisms (A) Glycolysis pathway with substrates that are hydrolyze by HADs: glucose 6-phosphate, fructose 6-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate. (B) Pentose phostphate pathway with substrates that are hydrolyze by HADs: glucose-6-phosphate, fructose-6-phosphate, dihydroxyacetone phosphate, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, gluconate 6-phosphate and erythrose-4-phosphate.
| Catalytic activity | N-acylneuraminate 9-phosphate + H2O = N-acylneuraminate + phosphate |
| Cofactor | Magnesium (By similarity) |
| Enzyme regulation | Inhibited by vanadate and calcium (By similarity) |
| Pathway | Carbohydrate metabolism; aminosugar metabolism |
| Similarity | Belongs to the haloacid dehalogenase-like hydrolase superfamily. NANP family |