Fascin Structure: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
[[Image:Fascin domains and conserved.png]] | [[Image:Fascin domains and conserved.png]] | ||
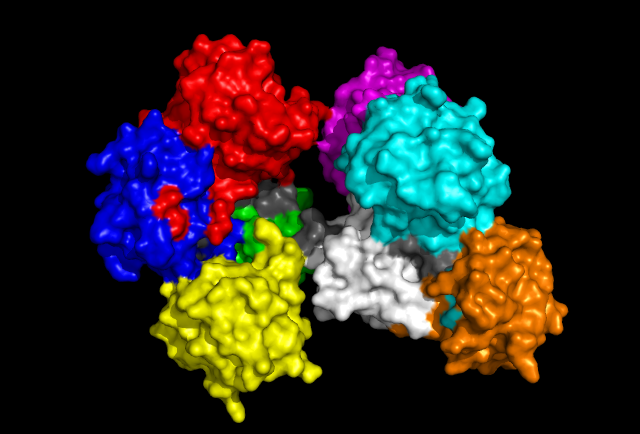
'Front' view of Fascin protein with each Fascin domain coloured. Grey colouration represents conserved residues found in sequence allignment. | 'Front' view of Fascin protein with each Fascin domain coloured. Grey colouration represents conserved residues found in sequence allignment. | ||
[[Image:Fascin domains and conserved back.png]] | [[Image:Fascin domains and conserved back.png]] | ||
| Line 17: | Line 19: | ||
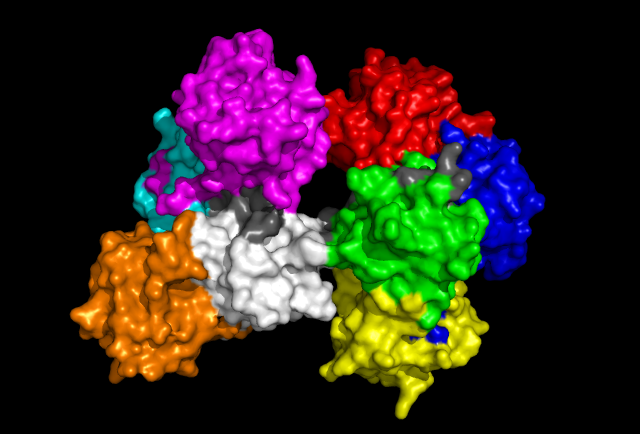
'Back' view of Fascin protein. Same colouration as above. | 'Back' view of Fascin protein. Same colouration as above. | ||
== Structual allignments == | |||
The dali database search returned several hundred similar structures to Fascin 1. | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 07:44, 10 June 2009
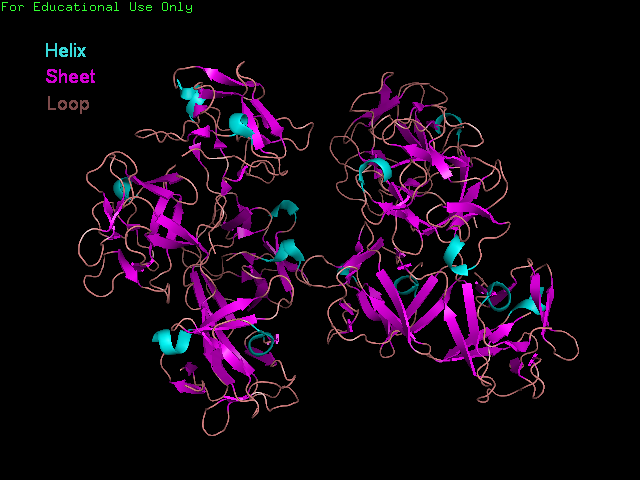
Fascin structure and domains
The human Fascin protein is a monomeric protein consisting of 8 repeats of the Fascin domain.
'Front' view showing secondary structure of Fascin.
'Front' view of Fascin protein with each Fascin domain coloured. Grey colouration represents conserved residues found in sequence allignment.
'Back' view of Fascin protein. Same colouration as above.
Structual allignments
The dali database search returned several hundred similar structures to Fascin 1.
References
Joe Dundas, Zheng Ouyang, Jeffery Tseng, Andrew Binkowski, Yaron Turpaz, and Jie Liang 2006. CASTp: computed atlas of surface topography of proteins with structural and topographical mapping of functionally annotated resiudes.Nucleic Acid Research, 34:W116-W118.
Dolinsky TJ, Nielsen JE, McCammon JA, Baker NA. PDB2PQR: an automated pipeline for the setup, execution, and analysis of Poisson-Boltzmann electrostatics calculations. Nucleic Acids Res, 32, W665-W667 (2004).