Function: Siowwei: Difference between revisions
From MDWiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| (18 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Results on Function Analysis''' | |||
2.1 Protein-interaction annotation | '''[[2.1 Protein-interaction annotation]]''' | ||
'''''Table 2.1''''' Complete annotation of NUBP2 retrieved from UnitProtKB/Swiss-Prot | |||
2. | '''Names and origin''' | ||
{| class="prettytable" | |||
| Protein names | |||
| '''Nucleotide-binding protein 2''''' Also known as:'' NBP 2 | |||
|- | |||
| Gene names | |||
| | |||
{| class="prettytable" | |||
| Name: | |||
| '''NUBP2''' | |||
|} | |||
|- | |||
| Organism | |||
| [http://beta.uniprot.org/taxonomy/9606 Homo sapiens (Human)] | |||
|} | |||
'''General annotation (Comments)''' | |||
{| class="prettytable" | |||
| Function | |||
| May contribute to formation of bipolar spindles (By similarity to ''E.coli'' MinD homolog). | |||
|- | |||
| Subunit structure | |||
| Binds NUBP1 and KIFC1 (By similarity). | |||
|- | |||
| Subcellular location | |||
| Nucleus (By similarity). Note=Associated with nucleus during interphase and nucleocytoplasm surrounding mitotic spindles during early mitosis. Enriched around centrosomes during late mitosis (By similarity). | |||
|- | |||
| Tissue specificity | |||
| Widely expressed with highest expression in skeletal muscle. | |||
|- | |||
| Developmental stage | |||
| Expressed in fetal brain, lung, liver and kidney. | |||
|- | |||
| Sequence similarities | |||
| Belongs to the [http://beta.uniprot.org/uniprot/?query=family:%22Mrp%2FNBP35+ATP-binding+proteins+family%22 Mrp/NBP35 ATP-binding proteins family]. | |||
|} | |||
'''Ontologies''' | |||
{| class="prettytable" | |||
| colspan="2" | '''Keywords''' | |||
|- | |||
| Cellular component | |||
| [http://beta.uniprot.org/keywords/539 Nucleus] | |||
|- | |||
| Ligand | |||
| [http://beta.uniprot.org/keywords/67 ATP-binding][http://beta.uniprot.org/keywords/547 Nucleotide-binding] | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="2" | '''Gene Ontology (GO)''' | |||
|- | |||
| Molecular function | |||
| [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ego/DisplayGoTerm?id=GO:0000166 Nucleotide binding] | |||
Traceable author statement. Source: ProtInc | |||
|} | |||
'''[[2.2 Sequence Analysis]]''' | |||
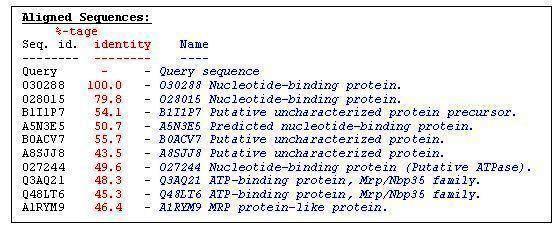
'''''Table 2.2 '''''Aligned sequence of 2ph1 protein | |||
[[Image:Ali.jpg]] | |||
'''[[2.3 Sequence motif (domain) analysis]]''' | |||
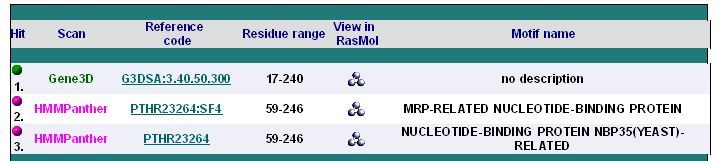
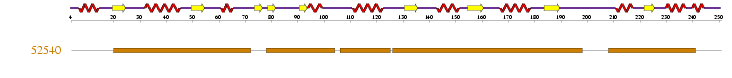
'''''Table 2.3''''' The diagram and table below show the '''3''' sequence motifs found in the sequence | |||
[[Image:3seq.jpg]] | |||
[[Image:3seq1.jpg]] | |||
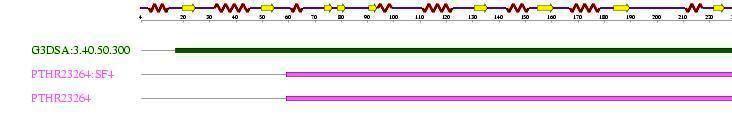
'''''Table 2.4 '''''The diagram and table below show the '''1''' sequence of superfamily found in the sequence | |||
[[Image:seq1.jpg]] | |||
[[Image:seq2.jpg]] | |||
'''[[2.4. Protein-protein interaction]]''' | |||
'''''Figure 1.'' '''Protein-protein interactions search using 2ph1 sequence | |||
<center>[[Image:inter1.jpg]]</center> | |||
<center>[[Image:input1.jpg]]</center> | |||
'''''Figure 2. '''''Protein-protein interactions search using ''NUBP2 ''sequence | |||
<center>[[Image:inter2.jpg]]</center> | |||
<center>[[Image:input2.jpg]]</center> | |||
'''[[2.5 Subcellular location]]''' | |||
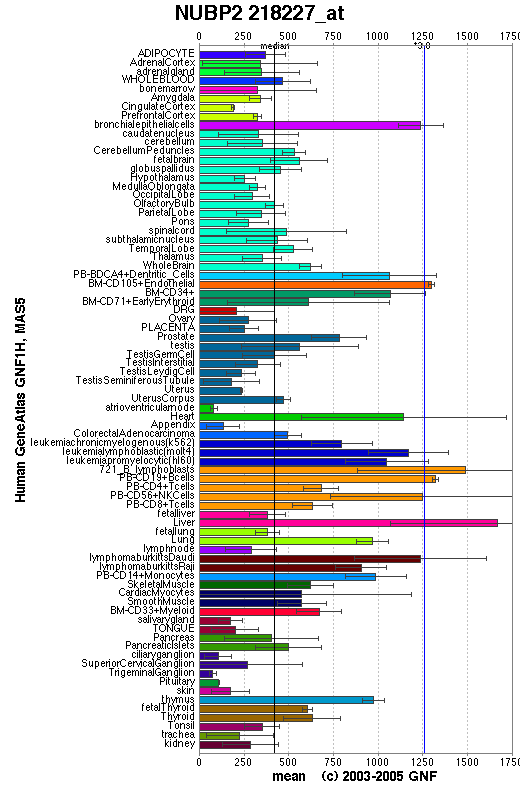
'''Figure 3.''' NUBP2 expressions in human and mouse tissues | |||
[[Image:exp.jpg]] | |||
Latest revision as of 05:37, 10 June 2008
Results on Function Analysis
2.1 Protein-interaction annotation
Table 2.1 Complete annotation of NUBP2 retrieved from UnitProtKB/Swiss-Prot
Names and origin
| Protein names | Nucleotide-binding protein 2 Also known as: NBP 2 | ||
| Gene names |
| ||
| Organism | Homo sapiens (Human) |
General annotation (Comments)
| Function | May contribute to formation of bipolar spindles (By similarity to E.coli MinD homolog). |
| Subunit structure | Binds NUBP1 and KIFC1 (By similarity). |
| Subcellular location | Nucleus (By similarity). Note=Associated with nucleus during interphase and nucleocytoplasm surrounding mitotic spindles during early mitosis. Enriched around centrosomes during late mitosis (By similarity). |
| Tissue specificity | Widely expressed with highest expression in skeletal muscle. |
| Developmental stage | Expressed in fetal brain, lung, liver and kidney. |
| Sequence similarities | Belongs to the Mrp/NBP35 ATP-binding proteins family. |
Ontologies
| Keywords | |
| Cellular component | Nucleus |
| Ligand | ATP-bindingNucleotide-binding |
| Gene Ontology (GO) | |
| Molecular function | Nucleotide binding
Traceable author statement. Source: ProtInc |
Table 2.2 Aligned sequence of 2ph1 protein
2.3 Sequence motif (domain) analysis
Table 2.3 The diagram and table below show the 3 sequence motifs found in the sequence
Table 2.4 The diagram and table below show the 1 sequence of superfamily found in the sequence
2.4. Protein-protein interaction
Figure 1. Protein-protein interactions search using 2ph1 sequence
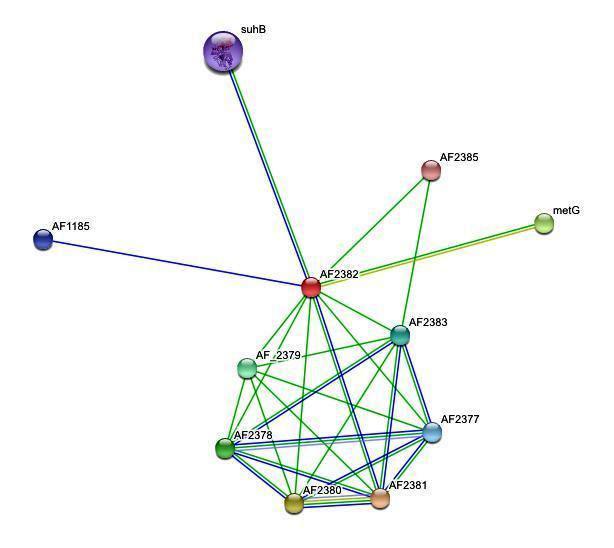
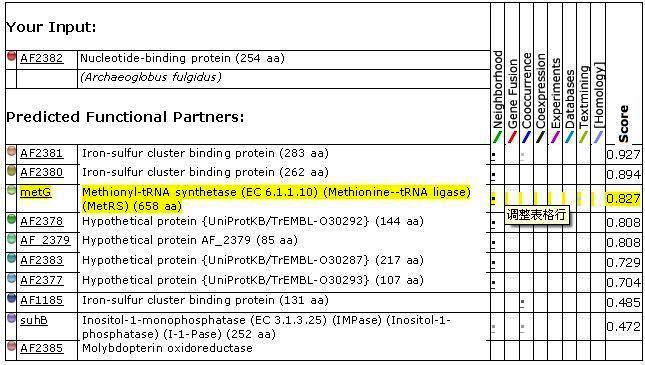
Figure 2. Protein-protein interactions search using NUBP2 sequence
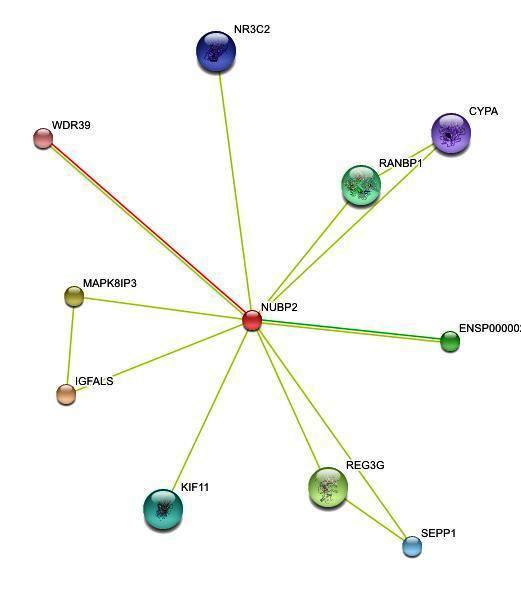
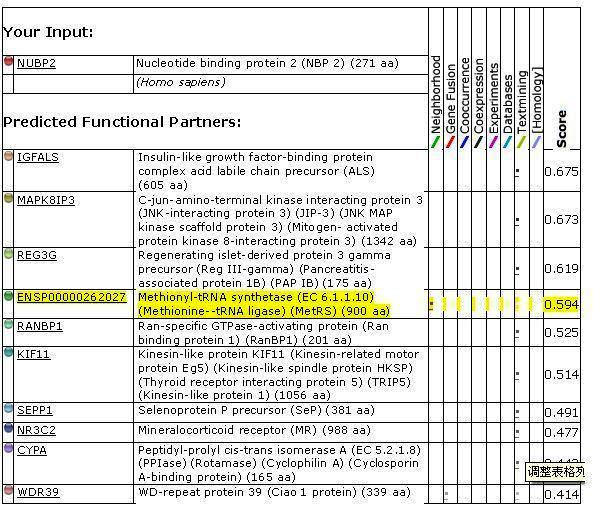
Figure 3. NUBP2 expressions in human and mouse tissues