|
|
| (54 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| [[Image:Mouse gene atlas.png]]
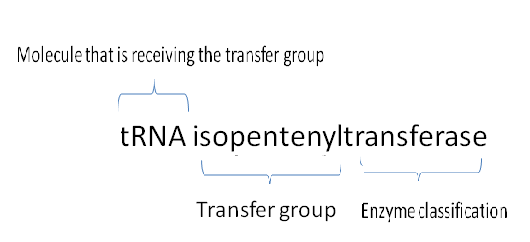
| | '''Function from its name''' |
|
| |
|
| | [[Image:reaction1.png|framed|center|none]] |
|
| |
|
| [[Image:Human geneAtlas.png]] | | [[How the enzyme act on tRNA| Next]] |
| | |
| Isopentenyltransferases (IPT) are enzymes that functions to catalyse the biosynthesis of cytokinins. Cytokinins are tRNA molecules containing modified adenine found at position 37 of the tRNA. An anticodon binding to codon encoding for uridine is found next to this modified adenine. This means that this modification occurs at the acceptor stem of tRNA molecules.This detailed and precise adenine modification is important in maintaining correct framework and the subsequent translation pathway.
| |
| | |
| Cytokinins are involved in several biochemical and cellular processes such as cell division and growth, both in plants and animals. They can exist in two forms; the tRNA-free and the tRNA-bound form, through addition of adenine to tRNA or AMP acceptor molecules. As the name suggest, tRNA-IPT adds adenine to tRNA molecules specifically to tRNA which binds to the codon encoded with uridine.
| |