Functional analysis of 2qgn: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
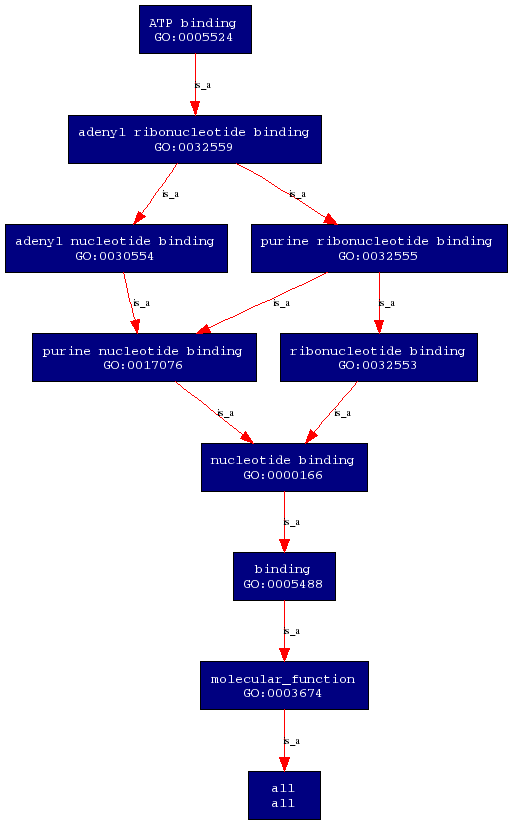
Molecular function of this enzyme is ATP binding. This means that the enzyme interacts selectively with ATP at the 5'end and acts as a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. | Molecular function of this enzyme is ATP binding. This means that the enzyme interacts selectively with ATP at the 5'end and acts as a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. | ||
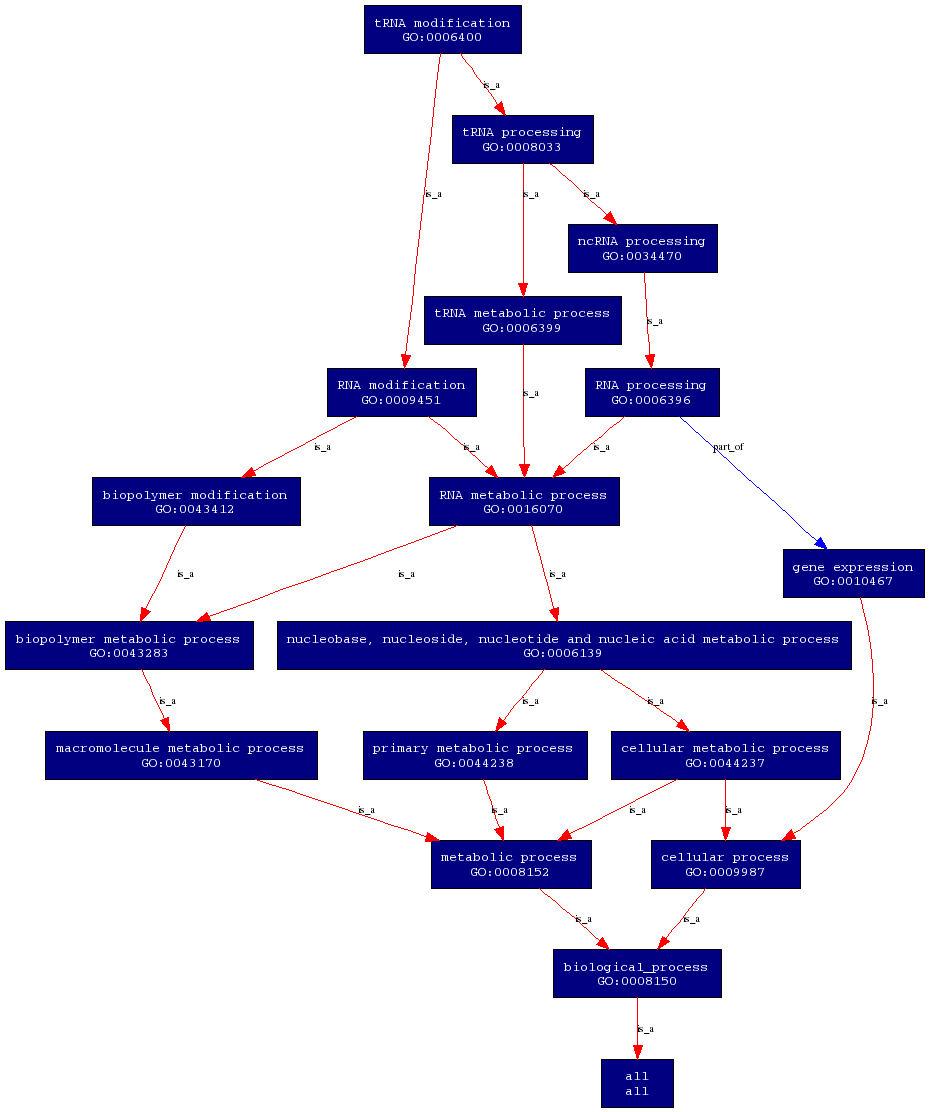
On the other hand, the biological process of this enzyme is tRNA modification. This involves the covalent alteration of one or more nucleotides within the tRNA, thus leading to a change in the properties of the tRNA. | On the other hand, the biological process of this enzyme is tRNA modification. This involves the covalent alteration of one or more nucleotides within the tRNA, thus leading to a change in the properties of the tRNA. | ||
'''Molecular Function''' | |||
[[Image:PROKNOW2- molecular function.png]] | |||
'''Biological Process''' | |||
[[Image:PROKNOW-biological process.png]] | |||
==Localisation of Expression== | ==Localisation of Expression== | ||
| Line 64: | Line 76: | ||
[[Image:motif.jpg]] | [[Image:motif.jpg]] | ||
Revision as of 07:38, 3 June 2008
Molecular function and biological processes of this enzyme was obtained from the ProKnow server. Molecular function of this enzyme is ATP binding. This means that the enzyme interacts selectively with ATP at the 5'end and acts as a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. On the other hand, the biological process of this enzyme is tRNA modification. This involves the covalent alteration of one or more nucleotides within the tRNA, thus leading to a change in the properties of the tRNA.
Molecular Function
Biological Process
Localisation of Expression
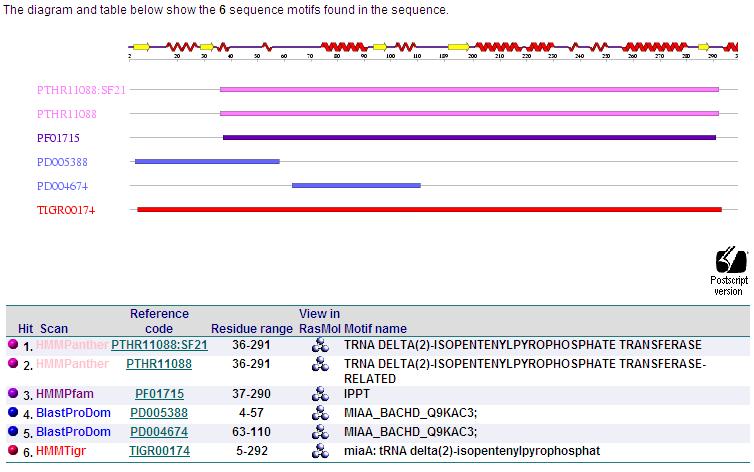
using the motif search, The C2-H2 Zinc finger motif found in tRNA-IPT also contributes to the enzyme's function. This motif is commonly found in nucleic acid-binding proteins and is composed of 25 to 30 amino acid residues.
Motif ZINC_FINGER_C2H2_1 in your sequence
Prosite ID: ZINC_FINGER_C2H2_1 (PS00028)
Description: Zinc finger C2H2 type domain signature.
Pattern: C-x(2,4)-C-x(3)-[LIVMFYWC]-x(8)-H-x(3,5)-H.
Appearance: Position Found Motif 396..418 CDLCDRIIIGDREWAAHIKSKSH
Sequence: MASVAAARAVPVGSGLRGLQRTLPLVVILGATGTGKSTLALQLGQRLGGEIVSADSMQVE GLDIITNKVSAQEQRICRHHMISFVDPLVTNYTVVDFRNRATALIEDIFARDKIPIVVGG TNYYIESLLWKVLVNTKPQEMGTEKVIDRKVELEKEDGLVLHKRLSQVDPEMAAKLHPHD KRKVARSLQVFEETGISHSEFLHRQHTEEGGGPLGGPLKFSNPCILWLHADQAVLDERLD KRVDDMLAAGLLEELRDFHRRYNQKNVSENSQDYQHGIFQSIGFKEFHEYLITEGKCTLE TSNQLLKKGIEALKQVTKRYARKQNRWVKNRFLSRPGPIVPPVYGLEVSDVSKWEESVLE PALEIVQSFIQGHKPTATPIKMPYNEAENKRSYHLCDLCDRIIIGDREWAAHIKSKSHLN QLKKRRRLDSDAVNTIESQSVSPDHNKEPKEKGSPGQNDQELKCSV
A schematic representation of a zinc finger domain is shown below:
x x
x x
x x
x x
x x
x x
C H
x \ / x
x Zn x
x / \ x
C H
x x x x x x x x x x
http://ca.expasy.org/cgi-bin/nicedoc.pl?PDOC00028
GENOMIC CONTEXT In bacteria, the gene encoding this enzyme is known as miaA while the human and S. cerevisaea is TRIT1 and mod5 respectively. Although gene name differ in different organisms, they all synthesize enzyme of the same function.
Sequence Motif