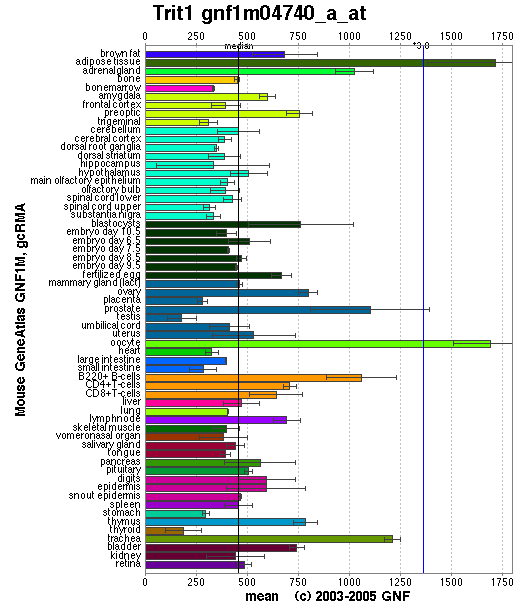
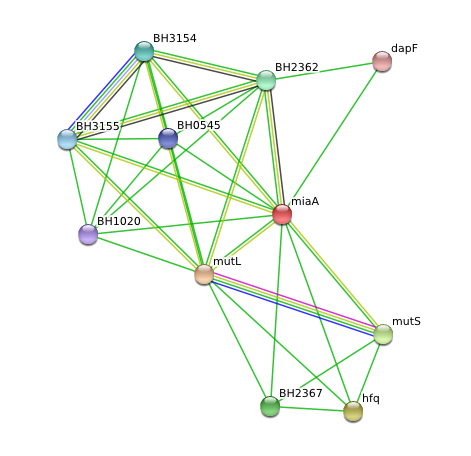
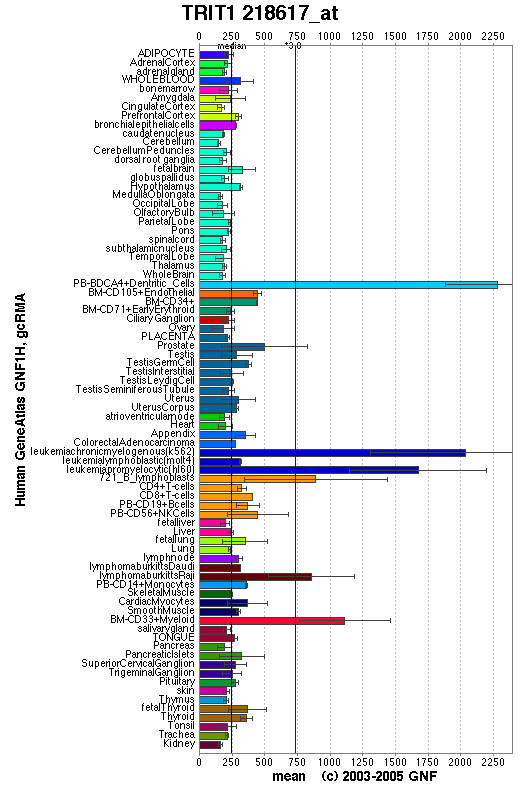
Functional analysis of 2qgn
Transferases are enzymes which transfer a group from a donor molecule to an acceptor molecule. As the name suggest, tRNA-IPT adds adenine to tRNA molecules specifically to tRNA, whose anticodon binds to the codon encoded with uridine. Below is the reaction catalysed by tRNA isopentenyltransferase.
Isopentenyl diphosphate + tRNA <=> diphosphate + tRNA containing 6-isopentenyladenosine
reaction taken from http://www.expasy.org/cgi-bin/nicezyme.pl?2.5.1.8
tRNA molecules with modified adenine specifically at position 37 are known as cytokinins.This modified adenine is found next to the anticodon that binds to the codon encoding for uridine. This detailed and precise adenine modification is important in maintaining correct framework and the subsequent translation pathway.
Cytokinins are involved in several biochemical and cellular processes such as cell division and growth, both in plants and animals. They can exist in two forms; the tRNA-free and the tRNA-bound form, through addition of adenine to tRNA or AMP acceptor molecules.
using the motif search, The C2-H2 Zinc finger motif found in tRNA-IPT also contributes to the enzyme's function. This motif is commonly found in nucleic acid-binding proteins and is composed of 25 to 30 amino acid residues.
A schematic representation of a zinc finger domain is shown below:
x x
x x
x x
x x
x x
x x
C H
x \ / x
x Zn x
x / \ x
C H
x x x x x x x x x x
http://ca.expasy.org/cgi-bin/nicedoc.pl?PDOC00028
The biological process of tRNA-IPT is trna metabolism. Generally, tRNAs are RNA molecules which is involved protein synthesis. They carry amino acids which corresponds to their anti-codon recognition sequence and adds them to the complementary codons along the length of the mRNA.