Introduction - 2qgnA
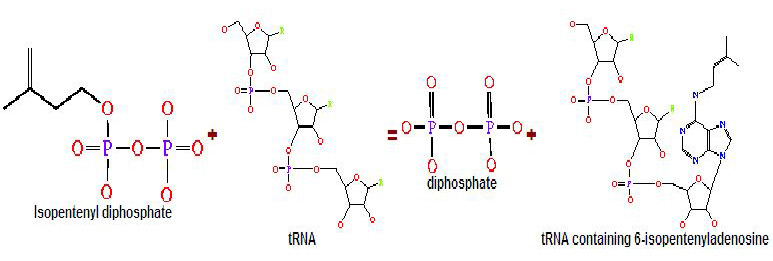
Cytokinins are first discovered in plants especially in meristematic regions and growing tissues. They function in cell division, cell differentiation and cell growth. Now, cytokinins are found also in tRNA of prokaryotes and eukaryotes. They can exist in two forms; the tRNA-free and the tRNA-bound form, through addition of adenine to tRNA or AMP acceptor molecules. Here, cytokinins are tRNA molecules with modified adenine bases. This modification is important as it stabilises and promotes efficient translational machinery. The enzyme that is responsible for the biosynthesis of these cytokinins in prokaryotes and eukaryotes is tRNA isopentenyltransferase (tRNA- IPT). This enzyme is also known as isopentenyl-diphosphate:trna isopentenyltransferase or tRNA delta(2)-isopentenylpyrophosphate transferase.
Generally, transferases are enzymes involved in tRNA metabolism, which encompasses tRNA breakdown, modification and synthesis. Essentially, this function is important in cellular processes such as protein synthesis. As for isopentenyltransferases, they transfer an isopentenyl group to the acceptor molecule. tRNA isopentenyltransferase (tRNA-IPT) as the name suggests transfers the isopentenyl group of dimethylallyl pyrophosphate to tRNA molecules. Specifically, it transfers an isopentenyl group onto adenine bases of tRNA molecules next to the anticodon which interacts with the codon encoding for uridine (Anna Golovko 2002). Modified adenine bases are commonly found at position 37 of the target tRNA.
The crystal structure of tRNA-IPT has been identified from Bacillus Halodurans (PDB code: 2QGN). Although the structure of the human tRNA-IPT has yet to be identified, the cDNA sequence has been recently cloned. Bioinformatic tools and analysis help to compare IPT protein sequences and structures from different organisms so that its evolution and structural conservation can be studied. This allows the function of this enzyme to be determined. Bioinformatic tools have helped to determine the possible functions of tRNA-IPT there are several conserved regions that might contribute to the functional role of these enzymes.