Introduction of SNAPG: Difference between revisions
From MDWiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
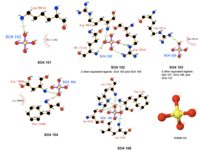
SNAPG protein structure obtained from ''Danio rerio'' organism comprises of 4 identical molecular chains (Chain A, B, C and D) interacting to one another via non-bonded contacts. Each chain is 307 amino acid residues in length and made of 69% helical secondary structure of 16 helices, 34 helix-helix interaction, 8 beta turns and 2 gamma turns[http://www.ebi.ac.uk/thornton-srv/databases/cgi-bin/pdbsum/GetPage.pl?pdbcode=2ifu&template=protein.html&o=SUMMARY&l=1&c=1&chain=A]. Two types of molecular component were observed to formed interactions with SNAPG molecule. These molecular components were sulfanate ion(SO4) and selenomethionine (MSE)(Figure 1). The sulfanate ions interact differently to different residues of different chain, unlike MSE in which included into SNAPG amino acid sequences as modified residue (Figure 2) | [[Image:Ligand structure visualisation.jpg|thumb|200px|right|Figure 1. Ligands interaction to SNAPG chain A. A) Ligands position in the structure are highlighted; B) Secondary structure of SNAPG chain A with ligands interaction indicated; and C) Various ligand interactions with SNAPG by covalent bonds (shown in red color), hydrogen bonding (cyan) and van der waals (green) ]] | ||
SNAPG protein structure obtained from ''Danio rerio'' organism comprises of 4 identical molecular chains (Chain A, B, C and D) interacting to one another via non-bonded contacts. Each chain is 307 amino acid residues in length and made of 69% helical secondary structure of 16 helices, 34 helix-helix interaction, 8 beta turns and 2 gamma turns[http://www.ebi.ac.uk/thornton-srv/databases/cgi-bin/pdbsum/GetPage.pl?pdbcode=2ifu&template=protein.html&o=SUMMARY&l=1&c=1&chain=A]. Two types of molecular component were observed to formed interactions with SNAPG molecule. These molecular components were sulfanate ion(SO4) and selenomethionine (MSE)(Figure 1). The sulfanate ions interact differently to different residues of different chain, unlike MSE in which included into SNAPG amino acid sequences as modified residue (Figure 1.B,C & 2). | |||
[[Image:Sulfate ion ligand interactions.png|thumb|200px|right|Figure 2. Various interaction of sulfanate ions]] | |||
Revision as of 00:33, 11 June 2007

Figure 1. Ligands interaction to SNAPG chain A. A) Ligands position in the structure are highlighted; B) Secondary structure of SNAPG chain A with ligands interaction indicated; and C) Various ligand interactions with SNAPG by covalent bonds (shown in red color), hydrogen bonding (cyan) and van der waals (green)
SNAPG protein structure obtained from Danio rerio organism comprises of 4 identical molecular chains (Chain A, B, C and D) interacting to one another via non-bonded contacts. Each chain is 307 amino acid residues in length and made of 69% helical secondary structure of 16 helices, 34 helix-helix interaction, 8 beta turns and 2 gamma turns[1]. Two types of molecular component were observed to formed interactions with SNAPG molecule. These molecular components were sulfanate ion(SO4) and selenomethionine (MSE)(Figure 1). The sulfanate ions interact differently to different residues of different chain, unlike MSE in which included into SNAPG amino acid sequences as modified residue (Figure 1.B,C & 2).