Methods for evolutionary analysis: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(Undo revision 14400 by Daniel Federr (Talk)) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
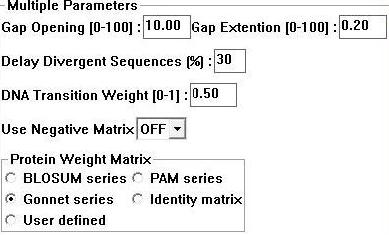
Sequences for evolutionary analysis were gathered from NCBI using BLAST (refseq). These were selected from different phyla on the basis of sequence identity (>30%). More distantly related sequences were obtained using the Psi-BLAST algorithm available at Interpro. Selected sequences were gathered in FASTA format and input into a .txt file sequentially. ClustalX 1.83 [ | Sequences for evolutionary analysis were gathered from NCBI using BLAST (refseq). These were selected from different phyla on the basis of sequence identity (>30%). More distantly related sequences were obtained using the Psi-BLAST algorithm available at Interpro. Selected sequences were gathered in FASTA format and input into a .txt file sequentially. ClustalX 1.83 [2] was then used to generate a multiple sequence alignment for the above sequences using the following parameters; | ||
[[Image:clus.jpg]] | [[Image:clus.jpg]] | ||
'''Figure 1:''' Clustalx 1.83 alignment parameters [ | '''Figure 1:''' Clustalx 1.83 alignment parameters [2] | ||
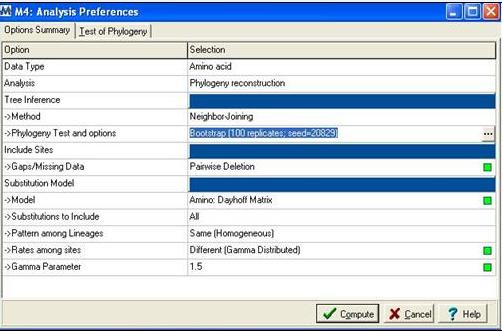
Following alignment; sequences were trimmed in Clustalx [ | Following alignment; sequences were trimmed in Clustalx [2] from residues 31-184 to remove extending ‘tails’ for more accurate phylogenetic analysis. The alignment file was then saved as an .aln file and exported to MEGA 4.0 [3] using the program’s conversion to MEGA format tool. MEGA [3] was then used to construct a bootstrapped neighbour joining tree using the following parameters; | ||
[[Image:mega.jpg]] | [[Image:mega.jpg]] | ||
'''Figure 2:''' Mega alignment parameters [ | '''Figure 2:''' Mega alignment parameters [3], Gamma parameter was established using Quartet puzzling [1]. | ||
A bootstrapped tree representing radiation was then copied to Microsoft power point 2007 to emphasise key features and significant bootstrap values. | A bootstrapped tree representing radiation was then copied to Microsoft power point 2007 to emphasise key features and significant bootstrap values. | ||
Latest revision as of 04:20, 15 June 2009
Sequences for evolutionary analysis were gathered from NCBI using BLAST (refseq). These were selected from different phyla on the basis of sequence identity (>30%). More distantly related sequences were obtained using the Psi-BLAST algorithm available at Interpro. Selected sequences were gathered in FASTA format and input into a .txt file sequentially. ClustalX 1.83 [2] was then used to generate a multiple sequence alignment for the above sequences using the following parameters;
Figure 1: Clustalx 1.83 alignment parameters [2]
Following alignment; sequences were trimmed in Clustalx [2] from residues 31-184 to remove extending ‘tails’ for more accurate phylogenetic analysis. The alignment file was then saved as an .aln file and exported to MEGA 4.0 [3] using the program’s conversion to MEGA format tool. MEGA [3] was then used to construct a bootstrapped neighbour joining tree using the following parameters;
Figure 2: Mega alignment parameters [3], Gamma parameter was established using Quartet puzzling [1].
A bootstrapped tree representing radiation was then copied to Microsoft power point 2007 to emphasise key features and significant bootstrap values.