Mz: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
----------- | ----------- | ||
== '''5. NUBP2 converged with MinD''' | == '''5. NUBP2 converged with MinD''' == | ||
(1) Similar functions | |||
(2) weak structural similarity | |||
--> Orthology or Convergence? | |||
Blast results and Nakashima et al. (1999), NUBP2 more related to MRP, not MiD (MRP/NUBP family) | |||
--> Convergence | |||
---- | ---- | ||
== '''6. NBP2 originated from NBP1''' | == '''6. NBP2 originated from NBP1''' == | ||
NBP1 group: plants and fungus, eukaryota | |||
NBP2 group: yeast and higher eukaryota | |||
--> broader expression of NBP1 in tissues and across domains | |||
--> NBP2 originates from the deletion of the cystein-rich N-terminal of NBP1 | |||
---- | ---- | ||
== ''' | == '''7. Evolution conlusions:''' == | ||
Revision as of 01:55, 10 June 2008
Why Evolution?
Gene VS Environment Interaction
- Divergence / Convergence
- Homology: Orthology / Paralog -- common ancestral genes
- Gene Duplication / Transfer
- Natural Selection
By studying protein evolutions, 1. The behavior of the genes / environment (Knowledge) 2. Artifical selection (Application)
1. Psi-BLAST search and sequences selection:
- Selected organisms (33) across the three domains include:
Archae (6) - A3 (Methanococcus voltae A3), 6A8 (Candidatus Methanoregula boonei 6A8), C.symbiosum (Cenarchaeum symbiosum A), GSS1 (Thermoplasma volcanium GSS1), A. fulgidus (Archaeoglobus fulgidus DSM 4304), uncultured (uncultured methanogenic archaeon RC-I)
Bacteria (7) - Goettinger (Syntrophomonas wolfei subsp. wolfei str. Goettingen), Lettingae (Thermotoga lettingae), ATCC 824 (Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824), MIT 9211 (Prochlorococcus marinus str. MIT 9211), BAV1 (Dehalococcoides sp. BAV1), DSM 4136 (Verrucomicrobium spinosum DSM 4136), DSM 245 (Chlorobium limicola DSM 245)
Eukaryota (20)- Red Rice Japanese / Indian (Oryza sativa), Neurospora (Neurospora crassa OR74A), C.reinhardtii (Chlamydomonas reinhardtii), C.Elegans (Caenorhabditis elegans), Thale cress (Arabidopsis thaliana), Fission yeast (Schizosaccharomyces pombe 972h-), Brewer’s yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae), Zebrafish (Danio rerio), Drosophila.pseudo (Drosophila pseudoobscura), Fruit Fly (Drosophila melanogaster), western clawed frog (Xenopus tropicalis), African clawed frog (Xenopus laevis), Chicken (gallus gallus), Mouse (mus mucus), Rat (Rattus norvegicus), Cow (Bos taurus), Chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes), Human (homo sapiens).
2. ClustalX - multiple sequence alignment and conserved motifs:
Figure 1: P-loop folding relies on at least two motifs, S-G-K-G(2)-V-G-K-[ST] and D-X-D-[VFLIM]-X-G.
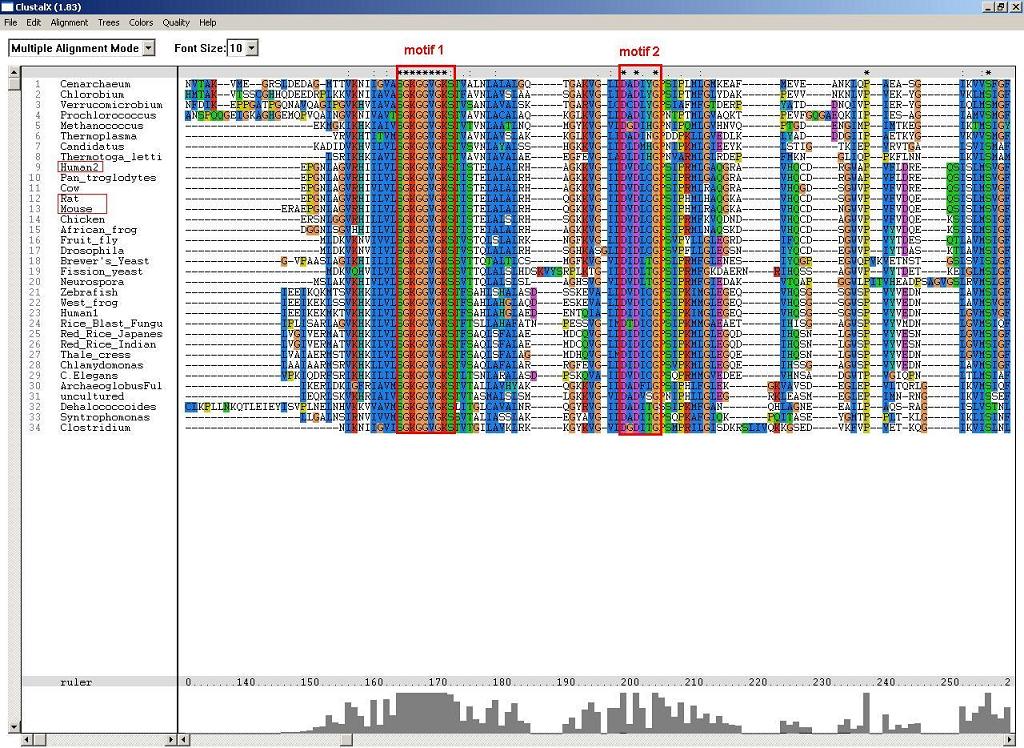
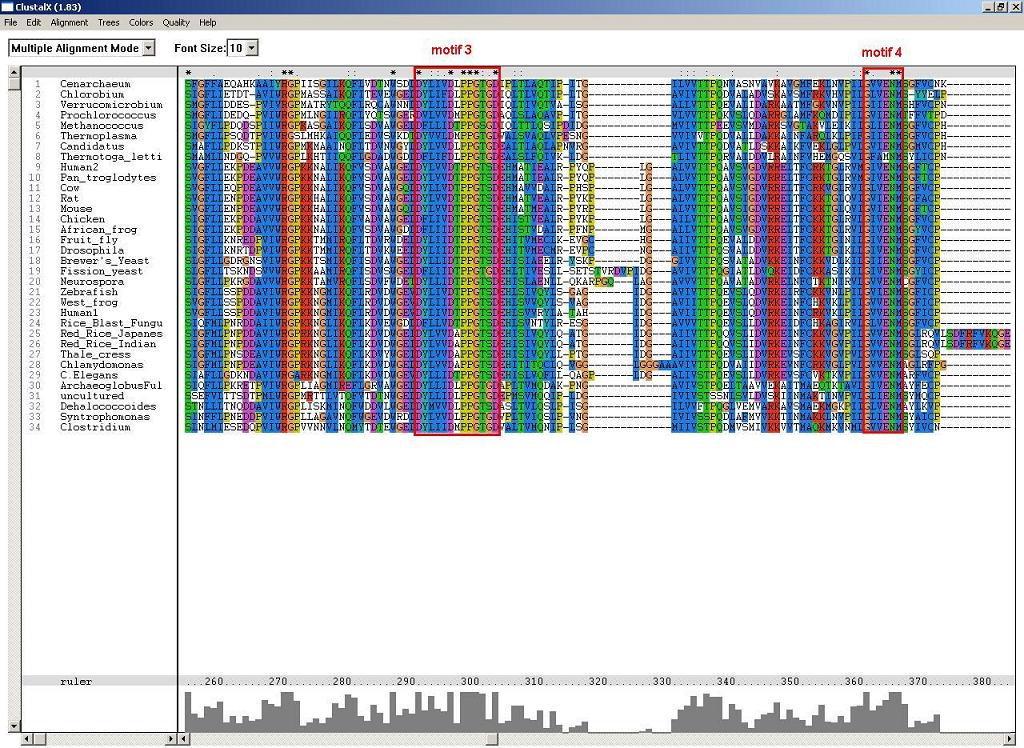
Figure 2: Another two conserved alpha and beta NUBP/MRP, which are likely to associate with the folding of p-loop components.
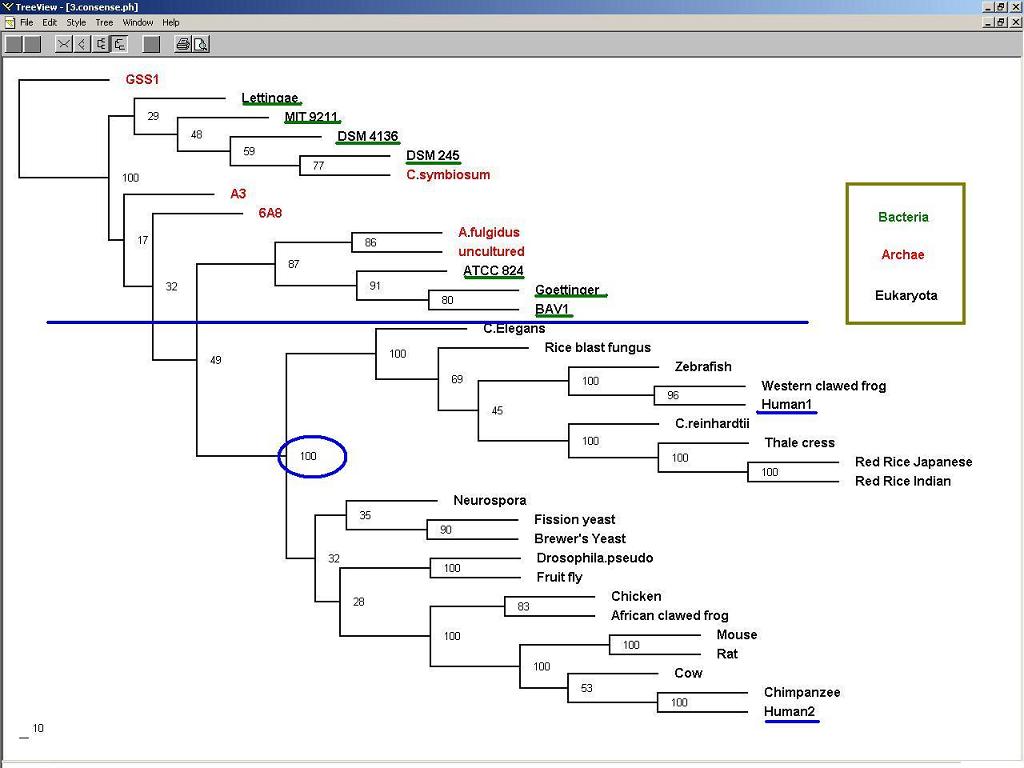
3. Phylogenic Trees and evolution:
Figure 3: Nucleotide binding protein 1 (long form) might appear earlier than nucleotide binding protein 2 (short form) during evolution.
4. Prokaryotic MRP proteins might be the paralogs to Human NUBP (1, 2).
(1) Functional differences:
prokaryotic MRP: Na+/H+ antiporter
eukaryotic NUBP: regulate the cycle of centrosome replication in concert with NUBP1 and KIFC5A (MinCD complex)
(2) Structural similarity:
Most human NUBP2 psi-BLAST results (proteins) possess MRP-like regions
(3) How MRP evolved into functionally distinct NUBP remain unclear.
5. NUBP2 converged with MinD
(1) Similar functions
(2) weak structural similarity
--> Orthology or Convergence?
Blast results and Nakashima et al. (1999), NUBP2 more related to MRP, not MiD (MRP/NUBP family)
--> Convergence
6. NBP2 originated from NBP1
NBP1 group: plants and fungus, eukaryota
NBP2 group: yeast and higher eukaryota
--> broader expression of NBP1 in tissues and across domains
--> NBP2 originates from the deletion of the cystein-rich N-terminal of NBP1