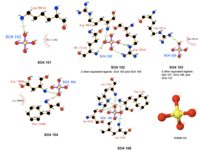
Result of SNAPG
SNAPG Structure
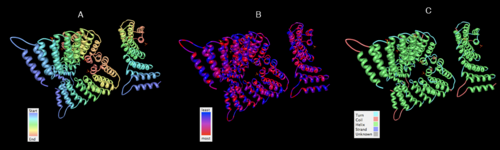
Structure architecture
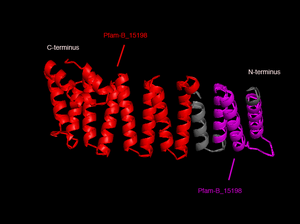
In order to analyze protein structure of SNAPG, structural comparison to known protein structure is required. An insight to SNAPG structural arrangement provides various informative data on possible protein functions and interactions with another protein and/or DNA. Based on protein families database, Pfam at Sanger, it was found that SNAPG protein matched to Pfam-B protein families and consist of 2 domains, Pfam-B_7270 (PB007270) and Pfam-B_15198 (PB015189) respectively as shown in Figure 3. Both of 2 domains appears to be associated with NSF attachment protein activity (*dijelasin di discussion aja! NSF acivity dijelasin ga?)[1].

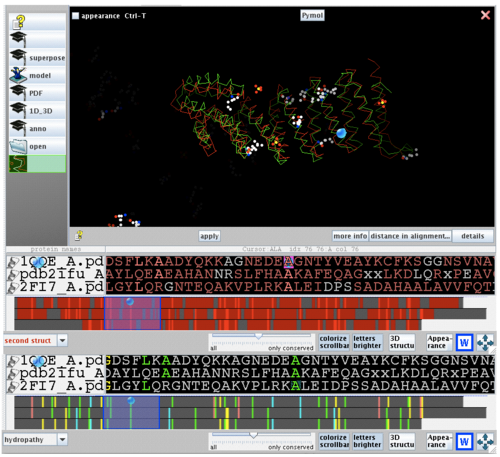
. The sequence was also used against InterproScan generated by Profunc that gave an TFR (Tetratricopeptide-like helical) domain classification while that of protein family agrees with Pfam classification.
(interproscan)
Structural comparison
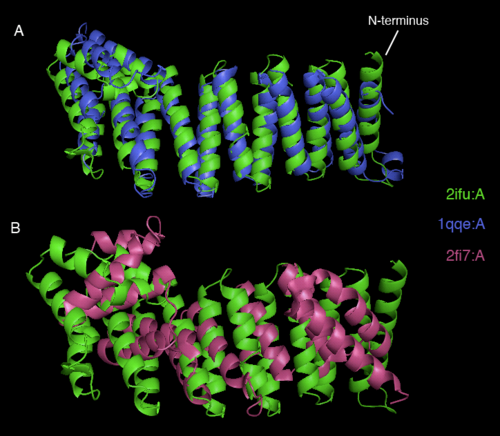
Dali webserver is one of the powerful tool to screen any protein that are structurally homologous with our query. Two structurally related proteins with highest Z-value generated by Dali server were chosen for SNAPG structure comparison analysis. These proteins were vesicular transport ptotein sec17 (1qqe) and type 4 fimbrial biogenesis protein (2f17) (refer to Table 1).alto
| PDB-chain | Structure | Z-value | % identity | Protein |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2IFU-A | 37.8 | 100 | Endocytosis/exocytosis. Gamma-SNAP (Danio rerio) | |
| 1QQE-A | 23.3 | 23 | Protein binding. Vesicular transport protein sec17(yeast) | |
| 2FI7-A | 12.9 | 14 | Protein transport. Type 4 fimbrial biogenesis protein pili (Pseudomonas aeruginosa) |
2ifuA, 1qqeA and 2fi7 alignment
physical properties
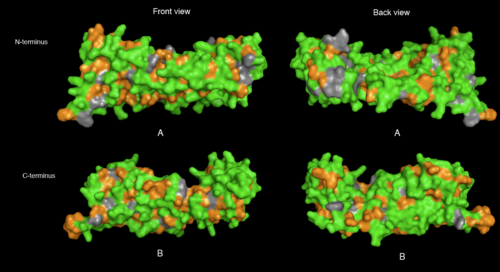
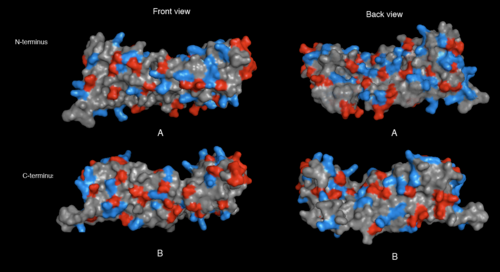
[[image:Electrostatic potential (molecular surface).png|thumb|left|500px|Figure 9. 2ifuA electrostatic potential map visualised by molecular surface. Computation method that were used are coulumb method.](red= -1.800; white= 0.000; blue= +1.800]
Figure 10 cleft