Michael Structure work: Difference between revisions
(New page: Week 4 work SCOP structural protein classification info: Protein: Fascin from Human (Homo sapiens) [TaxId: 9606] Lineage: 1. Root: scop 2. Class: All beta proteins [48724] 3. Fold: b...) |
No edit summary |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
1. Root: scop | 1. Root: scop | ||
2. Class: All beta proteins | |||
3. Fold: beta-Trefoil | 2. Class: All beta proteins | ||
4. duplication: has internal pseudo threefold symmetry | 3. Fold: beta-Trefoil barrel, closed; n=6, S=12; and a hairpin triplet; meander | ||
5. Family: Fascin | 4. duplication: has internal pseudo threefold symmetry Superfamily: Actin-crosslinking proteins | ||
6. Protein: Fascin | |||
5. Family: Fascin | |||
6. Protein: Fascin duplication: tandem repeat of four domains | |||
7. Species: Human (Homo sapiens) [TaxId: 9606] [50408] | 7. Species: Human (Homo sapiens) [TaxId: 9606] [50408] | ||
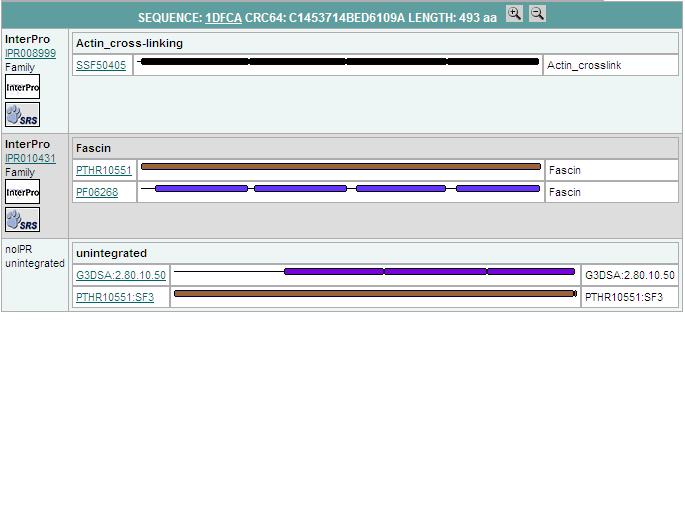
Interpro stuff: | |||
This family consists of several eukaryotic fascin or singed proteins. The fascins are a structurally unique and evolutionarily conserved group of actin cross-linking proteins. Fascins function in the organisation of two major forms of actin-based structures: dynamic, cortical cell protrusions and cytoplasmic microfilament bundles. The cortical structures, which include filopodia, spikes, lamellipodial ribs, oocyte microvilli and the dendrites of dendritic cells, have roles in cell-matrix adhesion, cell interactions and cell migration, whereas the cytoplasmic actin bundles appear to participate in cell architecture [1]. | |||
[[Image:interpro.jpg]] | |||
Latest revision as of 08:44, 26 May 2009
Week 4 work
SCOP structural protein classification info:
Protein: Fascin from Human (Homo sapiens) [TaxId: 9606]
Lineage:
1. Root: scop
2. Class: All beta proteins
3. Fold: beta-Trefoil barrel, closed; n=6, S=12; and a hairpin triplet; meander
4. duplication: has internal pseudo threefold symmetry Superfamily: Actin-crosslinking proteins
5. Family: Fascin
6. Protein: Fascin duplication: tandem repeat of four domains
7. Species: Human (Homo sapiens) [TaxId: 9606] [50408]
Interpro stuff:
This family consists of several eukaryotic fascin or singed proteins. The fascins are a structurally unique and evolutionarily conserved group of actin cross-linking proteins. Fascins function in the organisation of two major forms of actin-based structures: dynamic, cortical cell protrusions and cytoplasmic microfilament bundles. The cortical structures, which include filopodia, spikes, lamellipodial ribs, oocyte microvilli and the dendrites of dendritic cells, have roles in cell-matrix adhesion, cell interactions and cell migration, whereas the cytoplasmic actin bundles appear to participate in cell architecture [1].