Chromosome 1 open reading frame 41 Structure: Difference between revisions
From MDWiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
Hana Hamzah (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
''' | '''1)Structural similarities''' | ||
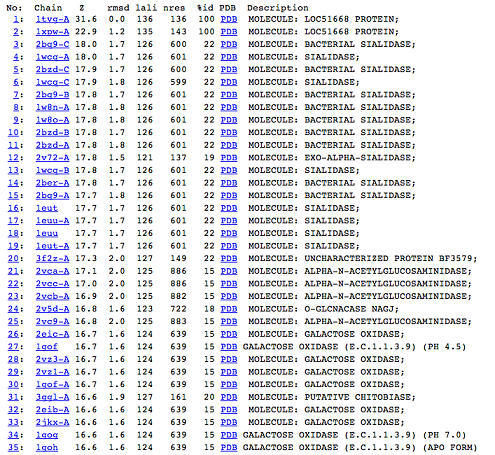
[[Image:Picture 1.png|centre|framed|'''Figure 5:''' DALI result showing the first 35 proteins that have similar structures to c1orf41. Even though the proteins are similar in structure they have very little sequence identity to c1orf41. 1xpw is c1orf41 but the structure was solved by NMR.]] | |||
'''2)Domain Classification''' | |||
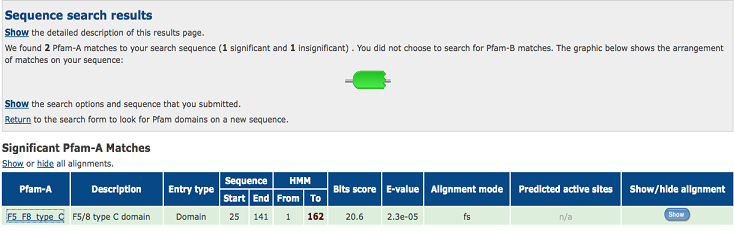
[[Image:1TVG pfam.png|centre|framed|'''Figure 6:''' Pfam result indicated that our protein has a F5/8 type C domain, also known as the discoidin domain which is apart of galactose binding domain super family.]] | |||
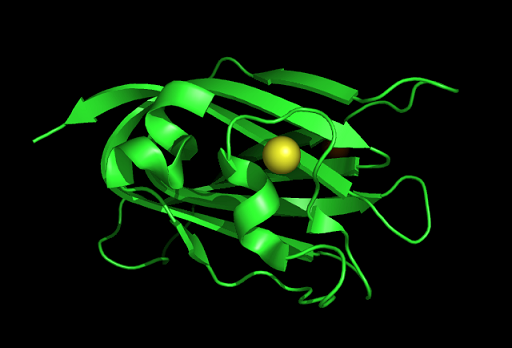
'''3)Protein Structure''' | |||
Secondary structure | Secondary structure | ||
| Line 17: | Line 27: | ||
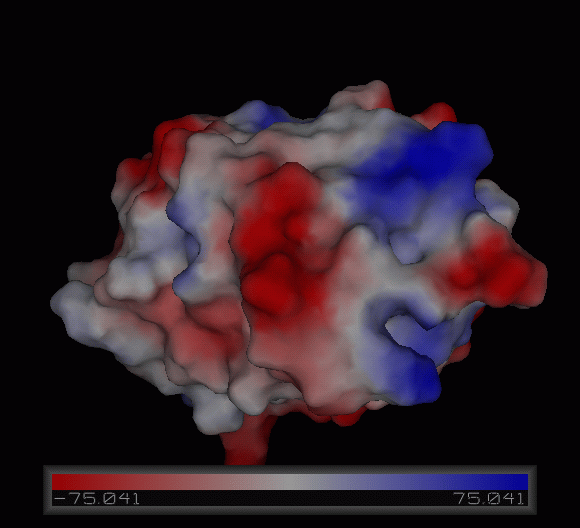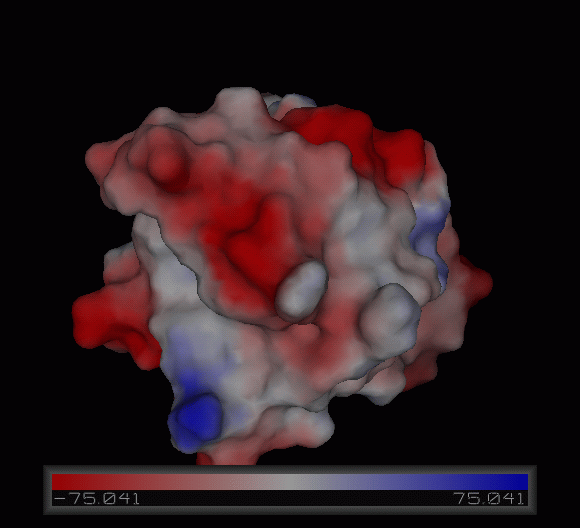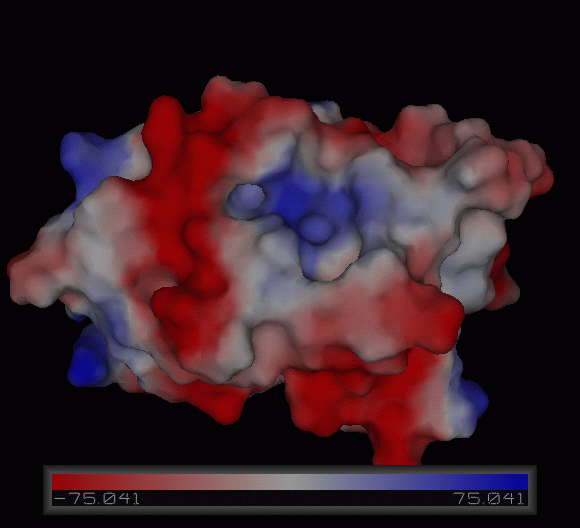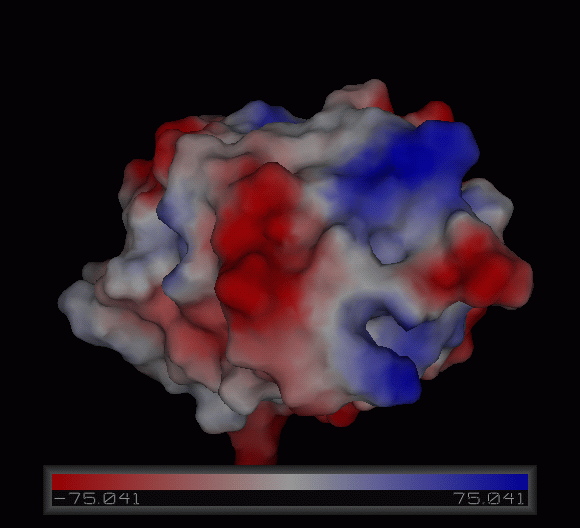
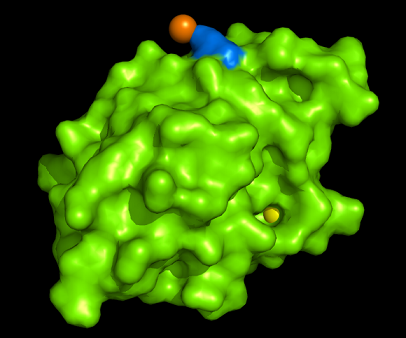
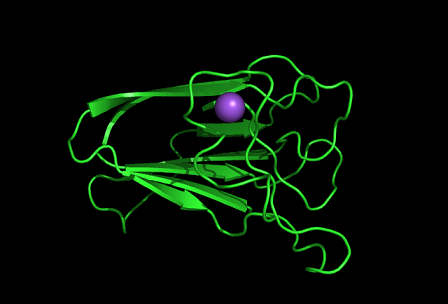
[[Image:1tvg surface.png|centre|framed|'''Figure 4:''' Surface representation of c1orf41. The Ca (II) ion is located within a pocket of the protein. Sm (III) interacts with Asp92 on the protein but its presence was probably due to the method used in solving the phase problem during structure solution using x-ray crystallogrophy.]] | [[Image:1tvg surface.png|centre|framed|'''Figure 4:''' Surface representation of c1orf41. The Ca (II) ion is located within a pocket of the protein. Sm (III) interacts with Asp92 on the protein but its presence was probably due to the method used in solving the phase problem during structure solution using x-ray crystallogrophy.]] | ||
''' | '''4)Possible ligand binding sites''' | ||
Revision as of 05:29, 16 June 2009
1)Structural similarities
2)Domain Classification
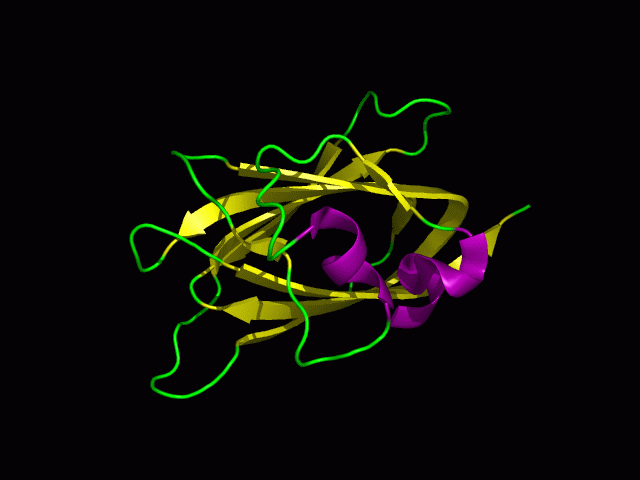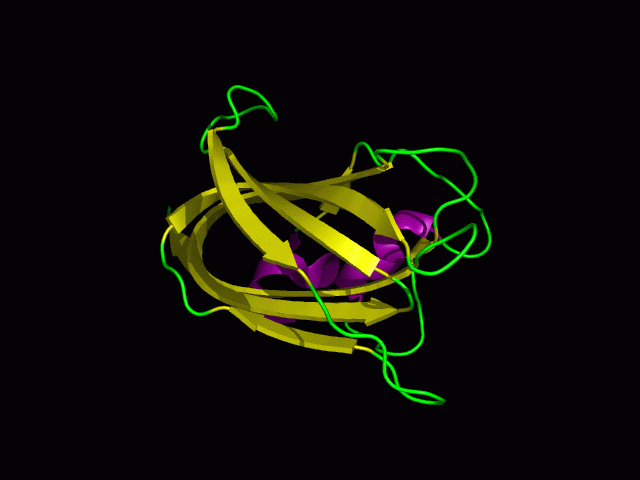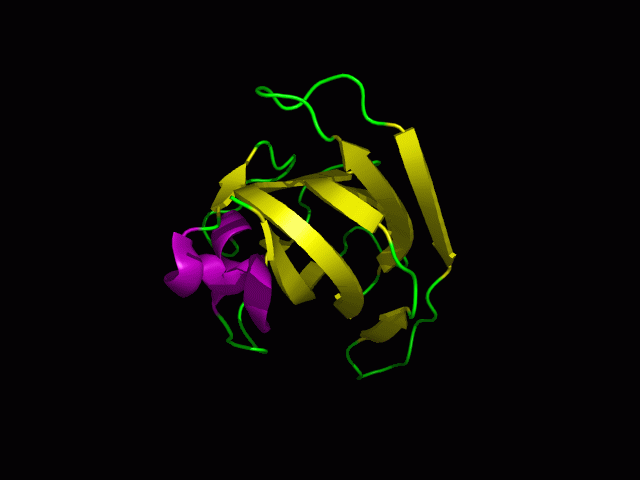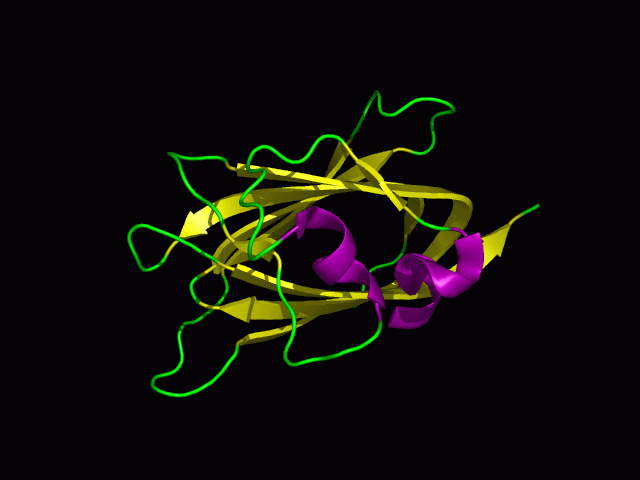
3)Protein Structure
Secondary structure
Tertiary structure
4)Possible ligand binding sites
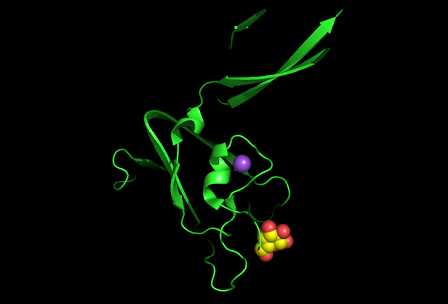
Figure 10:Pymol figure displaying possible metal binding position on c1orf41. Pink are the residues that may be involved in coordinating the metal and yellow is the calcium ion. The residues are based on CastP result. The aspartate and glutamate residues are likely to be important in binding positively charged metal ion
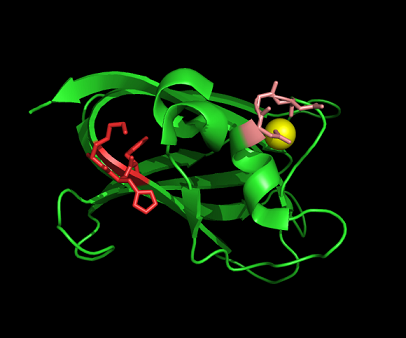
Figure 11:Nest 1 and 2 had scores higher than 2. So, they are more likely to be functional. His54 and Lys55 NH atoms are accessible from a large surface cleft of the protein. The cleft is also deep indicating that the nest is functionally important. The residues of Nest 2 are part of the loop that coordinates the Ca (II)ion.