Phostphatase: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
[[Image:Document19_08.png]] | [[Image:Document19_08.png]] | ||
'''Figure 19. ''' Alignment of rat and human Neu5Ac-9-P phosphatase with homologous sequences. The following sequences are aligned: ''Rattus | |||
norvegicus'' (Rnor, gi-34859431), ''Homo sapiens'' (Hsap, gi-23308749), ''Xenopus laevis'' (Xlae, gi-46250196), ''Danio rerio'' (Drer, gi- | |||
63101958), and ''Drosophila melanogaster'' (Dmel, gi-28381565). Only the first 280 residues of the latter sequence are shown. Completely | |||
conserved residues are shown in boldface type. Asterisks indicate the extremely conserved residues in phosphatases of the HAD family <sup>8</sup>. | |||
The MSA done by Maliekal ''et al'' shows that the Neu5Ac-9-Pase orthologs shared the three motifs found in phosphatases of the HAD family, | |||
namely a 1<sup>st</sup> motif comprising two extremely conserved aspartates (D), a 2<sup>nd</sup> motif comprising a conserved serine (S) or | |||
threonine (T), and a 3<sup>rd</sup> motif comprising a conserved lysine (K) and two conserved aspartates (D) <sup>8</sup>. The first aspartate | |||
in the first motif forms a phosphoaspartate during the catalytic cycle <sup>9</sup>. These findings suggested therefore that the HDHD4 protein | |||
was a phosphatase. The first aspartate in the first motif forms a phosphoaspartate during the catalytic cycle <sup>10</sup>. In our MSA (Figure | |||
16), the several conserved motifs that shared great similarity to the study done by Maliekal ''et al''. These findings suggested therefore that | |||
Neu5Ac-9-P phosphatase protein is a phosphatase | |||
*HAD (Haloacid dehalogenase-like) family | *HAD (Haloacid dehalogenase-like) family | ||
** Phosphatase activity: CO–P bond hydrolysis | ** Phosphatase activity: CO–P bond hydrolysis | ||
Revision as of 01:22, 12 June 2007
Phosphatase
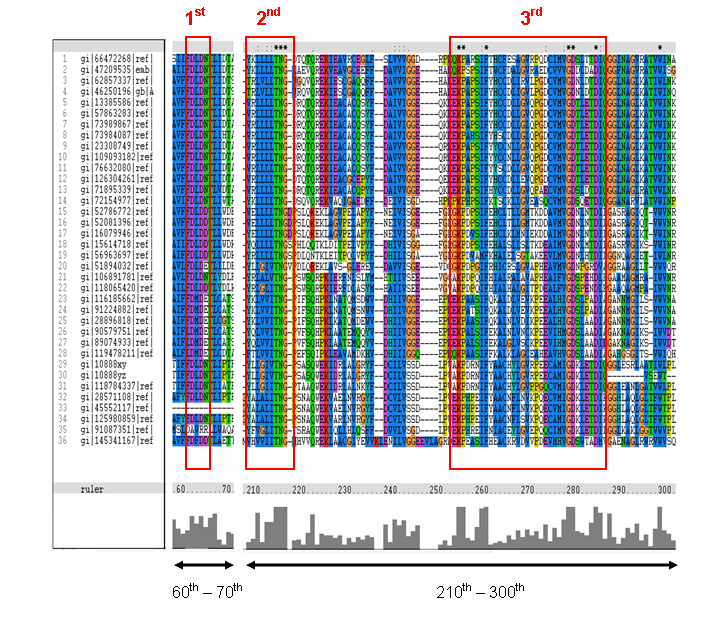
MSA of the 2gfh with 35 others proteins. Only the 60th – 70th and the 210th -300th amino acid
sequence were shown to illustrate the conserved and invariant regions. The 3 boxed-up sequences were either conserved or invariant regions.
- 1st - aspartic acid (D)
- 2nd - threonine (T), asparagine (N) and glycine (G)
- 3rd - lysine (K) and aspartates (D)
- MSA corelate with with study done by Maliekal et al
- N-acetylneuraminic acid phosphatase orthologs shared 3 motifs found in phosphatases
Figure 19. Alignment of rat and human Neu5Ac-9-P phosphatase with homologous sequences. The following sequences are aligned: Rattus
norvegicus (Rnor, gi-34859431), Homo sapiens (Hsap, gi-23308749), Xenopus laevis (Xlae, gi-46250196), Danio rerio (Drer, gi-
63101958), and Drosophila melanogaster (Dmel, gi-28381565). Only the first 280 residues of the latter sequence are shown. Completely
conserved residues are shown in boldface type. Asterisks indicate the extremely conserved residues in phosphatases of the HAD family 8.
The MSA done by Maliekal et al shows that the Neu5Ac-9-Pase orthologs shared the three motifs found in phosphatases of the HAD family,
namely a 1st motif comprising two extremely conserved aspartates (D), a 2nd motif comprising a conserved serine (S) or
threonine (T), and a 3rd motif comprising a conserved lysine (K) and two conserved aspartates (D) 8. The first aspartate
in the first motif forms a phosphoaspartate during the catalytic cycle 9. These findings suggested therefore that the HDHD4 protein
was a phosphatase. The first aspartate in the first motif forms a phosphoaspartate during the catalytic cycle 10. In our MSA (Figure
16), the several conserved motifs that shared great similarity to the study done by Maliekal et al. These findings suggested therefore that
Neu5Ac-9-P phosphatase protein is a phosphatase
- HAD (Haloacid dehalogenase-like) family
- Phosphatase activity: CO–P bond hydrolysis
- Dehalogenase activity: C–halogen bond hydrolysis
- Phosphonatase: C–P bond hydrolysis
- Phosphoglucomutase: CO–P bond hydrolysis and intramolecular phosphoryl transfer