Evolution ERp18: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
*multiple sequence alignment, | *multiple sequence alignment, | ||
*phylogenetic tree generation, | *phylogenetic tree generation, | ||
*bootstrapping, | *bootstrapping, and, | ||
*viewing and editing of phylogenetic trees | *viewing and editing of phylogenetic trees | ||
All of which were important to this assignment. | All of which were important to this assignment. | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
==Results== | ==Results== | ||
===Sequence | ===Sequence Collection=== | ||
The defining motif for a protein in the thioredoxin protein superfamily is the CXXC motif, with the two cystines representing the catalytic residues. It has been suggested in literature the the 'wild card' proteins between the cystines, in part, dictacts the specific molecular function (see [[Function ERp18]]). | |||
===Phylogenetic Trees=== | ===Phylogenetic Trees=== | ||
Revision as of 12:53, 15 June 2009
This page discusses the evolution of the target protein, Endoplasmic reticulum thioredoxin superfamily member.
Introduction
importance of evolution
Methods
To generate a collection of sequences which were, apparently, related to the target protein (ERp18), a PSI-Blast search was conducted. PSI-BLAST is advantageous as it uses an iterative approach whereby selected, relavent results from previous searches are used to inform the next search operation. The PSI-BLAST method was particularly useful in this circumstance since ERp18 is part of a superfamily of proteins and so has many homologues which have high identity scores and low e-vaulues but are actually different proteins.
The collected sequences were analysed using the MEGA4 suite. This program packages allows:
- multiple sequence alignment,
- phylogenetic tree generation,
- bootstrapping, and,
- viewing and editing of phylogenetic trees
All of which were important to this assignment.
The Dayhoff Matrix was used to generate phylogenetic trees throughout this analysis
Results
Sequence Collection
The defining motif for a protein in the thioredoxin protein superfamily is the CXXC motif, with the two cystines representing the catalytic residues. It has been suggested in literature the the 'wild card' proteins between the cystines, in part, dictacts the specific molecular function (see Function ERp18).
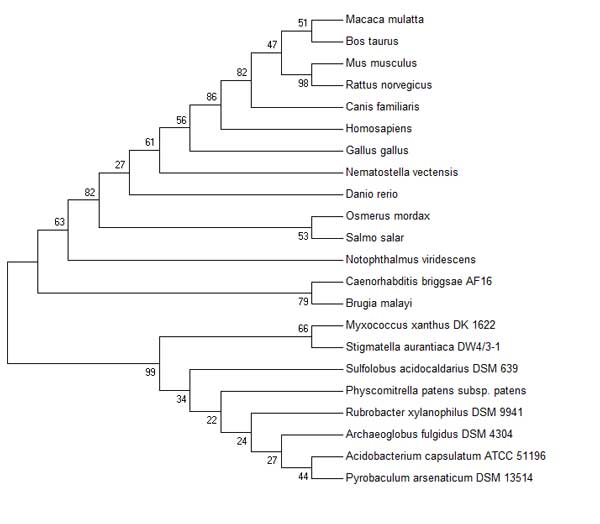
Phylogenetic Trees
add other zoomed in trees
Discussion
related to what organisms?
distant from other orgaisms?
important enzyme?