LOC56985 results
Evolution
The ClustalX multiple sequence alignment showed various residues that were conserved throughout all species, these are indicated by a '*' above the sequences. These residues are likely play an important role in the structure of the protein.
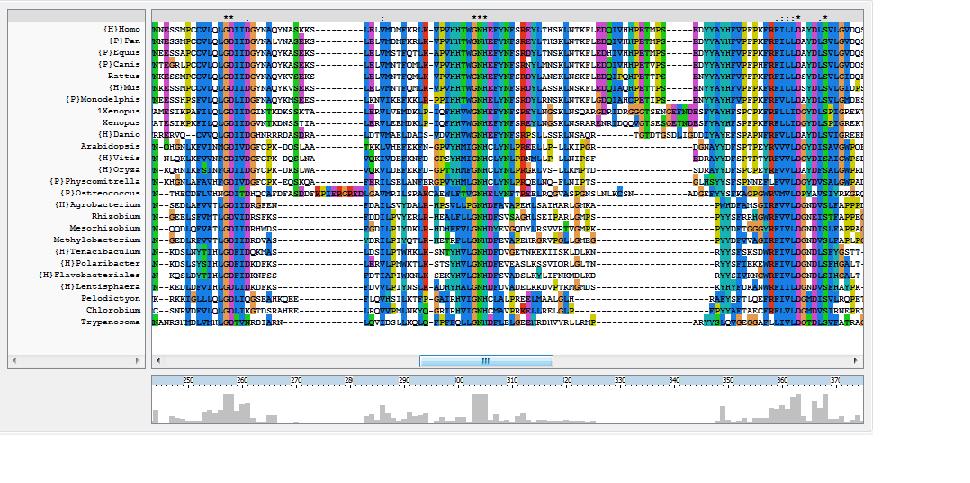
This picture only shows part of the multiple sequence alignment attained through ClustalX. To see the full alingnment click here.
Protein Tree
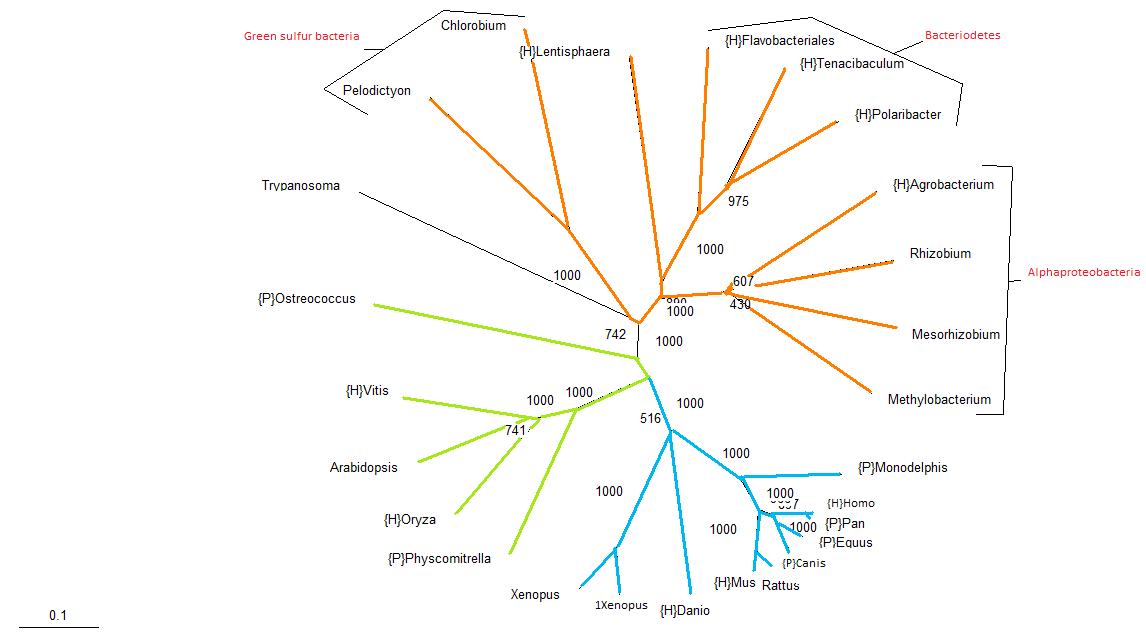
| Protein Tree for LOC56985 |
|---|
Key: Orange = bacteria, green = plants and blue = vertebrates.
The protein tree produced from the aligned sequences is analogous with traditional phylogenetic trees, with the exception of the Trypanosoma. Trypanosoma is a parasitic protozoa, which means that it is an eukaryote. In this tree it has been classified along with the bacteria. The bootstrap value for its position in the tree is relatively high at almost 75%, suggesting that perhaps Trypanosoma has acquired this protein by means of lateral transmission. Apart from that single exemplified organism, given the similarity of this protein tree with traditional taxonomy groupings, it seems likely that the usual mode of inheritance for this protein is through vertical transmission.
Bootstrapping values are considerably high, with most branches having a value of greater than 60% and only one branch in the alphaproteobacteria group having less than a 50% confidence.
Structure
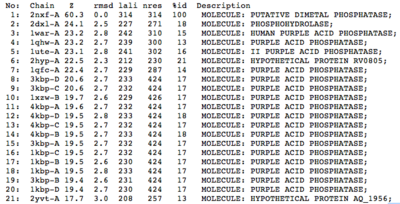
A structural comparison search of the Danio rerio ortholog (2nxf) showed that the gene product had its greatest similarity to a phosphorhydrolase and to various purple acid phosphatases (figure 1). All of these protein matches showed little sequence similarity to the 2nxf however the Z-score of these proteins were significant based on the guide given on the Dali server that Z-scores below 2.5 are insignificant matches. The top hit, 2dxl-A, showed a Z-score of 24.1; other members in the top five matches again showed Z-scores of above 20. Dali works by fitting the two structures together and determining how far apart each of the atoms are from one another to give a root mean square deviation (rmsd), even in the lowest of the top 20 matches the rmsd is 3.0 or below.
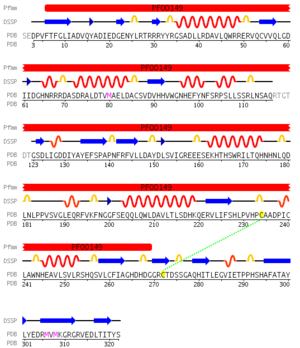
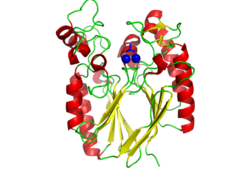
Pfam analysis shows a common domain to all these proteins as being a calcineurin-like phosphoesterase (PF00149). SCOP classification (Murzin et al 1995) of the protein shows it to be an Alpha and Beta (a + b) protein with a 4-layer sandwich fold of alpha/beta/beta/alpha (Figure 4), in the family of puple acid phosphatases (56301). The secondary structure assignment (Kabsch & Sander, 1983) show that the protein contains 20 beta-sheets, 12 alpha-helices and a single disulfide bond between Cys272 and Cys234 (Figure 2); the Pfam domain is shown to stretch from Phe6 to Gly269.
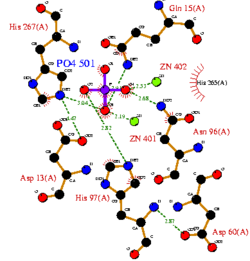
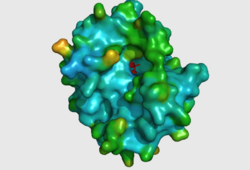
CASTp predicts that the protein contains a number of cavities the largest of which has a volume of 2043.1 covering an area of 950.8. This cavity is very large compared to the others predicted by CASTp. PyMOL analysis of this pocket shows that it is the binding site for the PO4 ligand and contains two Zn atoms buried in the pocket (Figure 3). This site shows three identical residues across the top five protein matches by Dali. This includes the human homolog as well as the Enterbacter aerogenes protein. The sequence of residues is GNH at positions 95 to 97, is unchanged, with a highly conserved acidic amino acid at position 98 down stream of this pattern. The ribbon view (Figure 4) shows that the ligands are positioned at the mid-point sandwiched between the two halves of the protein, above the inner beta-sheet centre of the protein. What only becomes apparent by looking at the surface view of the protein is that this cavity is bridged across the top to form a circle or donut shaped cavity (Figure 3), this may have implications for the type of substrate that can bind to this cavity. A close inspection of the binding site reveals that the GNH pattern appears to be directly involved with ligand binding (Figure 5). The binding site and interactions for the phosphate ion consists of Asp13, Gyn15, Asp60, Asp96, His97, His267 as well as interactions with the two Zn ions. Two residues, Asp96 and His97 form part of the GNH pattern seen in this class of proteins, Gly95 or the acidic amino acid at position 97 does not appear to interact directly with either the Zinc cofactors or the PO4 ligand, it may be that they are important in positioning the other two residues for their bonding interactions or creating the correct fold for the protein.
Abstract | Introduction | Results | Discussion | Conclusion | Method | References