Endoplasmic reticulum thioredoxin superfamily member: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[ | ==Contents== | ||
*[[Introduction ERp18]] | |||
*[[Evolution ERp18]] | |||
*[[Structure ERp18]] | |||
*[[Function ERp18]] | |||
*[[Conclusion ERp18]] | |||
==Abstract== | |||
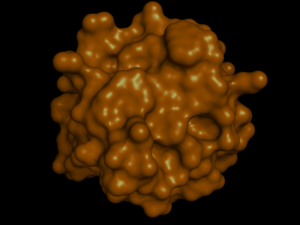
[[Image:General_structure_of_protein.png|thumb|'''Figure 1:''' The protein of interest - ERp18, an endoplasmic reticulum thioredoxin-like protein. ''Image produced using PyMOL.'']]<BR> | [[Image:General_structure_of_protein.png|thumb|'''Figure 1:''' The protein of interest - ERp18, an endoplasmic reticulum thioredoxin-like protein. ''Image produced using PyMOL.'']]<BR> | ||
| Line 5: | Line 12: | ||
The protein of interest for this research project was an endoplasmic reticulum thioredoxin superfamily member with an abbreviated name of ERp18 (short for 'endoplasmic reticulum protein with molecular weight of 18 kDa'). Study of ERp18 was broken into three areas: evolution, structure, and function. Structural analysis supported ERp18's classification as a thioredoxin protein. 3D modelling identified a catalytic site pertaining to an area of high evolutionary conservation. This catalytic site contained a CXXC residue motif - ubiquitous of all thioredoxin proteins. Furthermore, binding pockets were identified at the catalytic site by several bioinformatics programs. A DALI search identified numerous thioredoxin and thioredoxin-like proteins as being structurally similar, supporting the classification of ERp18 as a thioredoxin. Furthermore, information about the conformation and folding of ERp18 identified a thioredoxin fold. Recent literature has identified ERp18 as a dimer with a single protein molecular weight of 16.4 kDa, leading to the renaming of ERp18 as ERp16. | The protein of interest for this research project was an endoplasmic reticulum thioredoxin superfamily member with an abbreviated name of ERp18 (short for 'endoplasmic reticulum protein with molecular weight of 18 kDa'). Study of ERp18 was broken into three areas: evolution, structure, and function. Structural analysis supported ERp18's classification as a thioredoxin protein. 3D modelling identified a catalytic site pertaining to an area of high evolutionary conservation. This catalytic site contained a CXXC residue motif - ubiquitous of all thioredoxin proteins. Furthermore, binding pockets were identified at the catalytic site by several bioinformatics programs. A DALI search identified numerous thioredoxin and thioredoxin-like proteins as being structurally similar, supporting the classification of ERp18 as a thioredoxin. Furthermore, information about the conformation and folding of ERp18 identified a thioredoxin fold. Recent literature has identified ERp18 as a dimer with a single protein molecular weight of 16.4 kDa, leading to the renaming of ERp18 as ERp16. | ||
==Contents== | |||
*[[Introduction ERp18]] | |||
[[Introduction ERp18]] | *[[Evolution ERp18]] | ||
*[[Structure ERp18]] | |||
[[Evolution ERp18]] | *[[Function ERp18]] | ||
*[[Conclusion ERp18]] | |||
[[Structure ERp18]] | |||
[[Function ERp18]] | |||
[[Conclusion ERp18]] | |||
Revision as of 23:10, 15 June 2009
Contents
Abstract
The protein of interest for this research project was an endoplasmic reticulum thioredoxin superfamily member with an abbreviated name of ERp18 (short for 'endoplasmic reticulum protein with molecular weight of 18 kDa'). Study of ERp18 was broken into three areas: evolution, structure, and function. Structural analysis supported ERp18's classification as a thioredoxin protein. 3D modelling identified a catalytic site pertaining to an area of high evolutionary conservation. This catalytic site contained a CXXC residue motif - ubiquitous of all thioredoxin proteins. Furthermore, binding pockets were identified at the catalytic site by several bioinformatics programs. A DALI search identified numerous thioredoxin and thioredoxin-like proteins as being structurally similar, supporting the classification of ERp18 as a thioredoxin. Furthermore, information about the conformation and folding of ERp18 identified a thioredoxin fold. Recent literature has identified ERp18 as a dimer with a single protein molecular weight of 16.4 kDa, leading to the renaming of ERp18 as ERp16.