Methods for evolutionary analysis
The methods employed to obtain evolutionary data on selenium binding protein 2ece
The aim to the evolutionary analysis is to find and categorize similar proteins to hint towards the proteins likely function and role, as well as giving solid evidence to base our conclusions on. A series of steps were taken in order to accomplish this goal, these are listed below.
Psi Blast
The amino acid sequence of 2ece was put into a psi blast program using a non redundant database of proteins both the program and database was on the dvd. The amino acid sequence is below
MAIVPFKRDPTFYPSPKMAMKAPPEDLAYVACLYTGTGINRADFIAVVDVNPKSETYSKIVHKVELPYINDELHHFGWNA CSSALCPNGKPNIERRFLIVPGLRSSRIYIIDTKPNPREPKIIKVIEPEEVKKVSGYSRLHTVHCGPDAIYISALGNEEG EGPGGILMLDHYSFEPLGKWEIDRGDQYLAYDFWWNLPNEVLVSSEWAVPNTIEDGLKLEHLKDRYGNRIHFWDLRKRKR IHSLTLGEENRMALELRPLHDPTKLMGFINMVVSLKDLSSSIWLWFYEDGKWNAEKVIEIPAEPLEGNLPEILKPFKAVP PLVTDIDISLDDKFLYLSLWGIGEVRQYDISNPFKPVLTGKVKLGGIFHRADHPAGHKLTGAPQMLEISRDGRRVYVTNS LYSTWDNQFYPEGLKGWMVKLNANPSGGLEIDKEFFVDFGEARSHQVRLSGGDASSDSYCYP
The output blast file from the psi blast program can be found here Media:blast.txt
The blast file gives many unique, significant proteins from different organisms. A select few were taken from this blast file to be used in an alignment program
Clustalx
The selected proteins from a diverses selection of organisms were put into clustalx program to be aligned. Clustalx did a complete alignment and its output can be found here Media:Alignment.txt This alignment was then used to get a phylogenic tree and bootstrap values using phylip programs provided on the dvd.
Phylip Programs
The protdist program was used to calculate branch distances from the phylip output file of the msa. This program calculated the distance bases on the PAM method. The results can be found here Media:protdist1.txt.
The neighbor program was then used to construct a tree using the neighbour joining method Media:neighbortree.txt. The program calculated the tree while randomizing the input order. This tree was then inspected, and made ready for the bootstrap calculations.
The initial bootstrap calculations were done by seqboot using 100 iterations, to create a new alignment file Media:Align2.txt noticing some difference in the alignment. This was then sent to protdist to create another distance matrixMedia:protdist2.txt also with some difference to the original distance matrix. This distance matrix was then run through neighbor to calculate another tree Media:neighbourtree2.txt
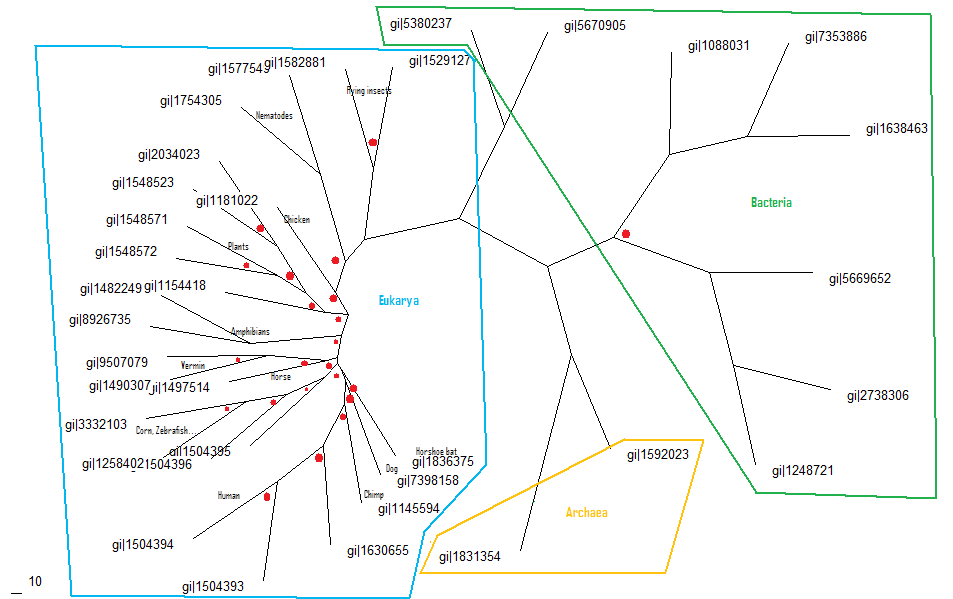
Consense was then used to show a phylogenic tree with branch lengths and bootstrap values Media:consense.txt
Which was then prepared into the final phylogenic tree below