Pyridoxal Phosphatase Results: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
YongMingLim (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Evolution''' | '''Evolution''' | ||
---- | ---- | ||
[[Image:Pyridoxal_phosphatase_MSA_page_1.jpg]] | |||
[[Image:Pyridoxal_phosphatase_MSA_page_2.jpg]] | |||
[[Image:Pyridoxal_phosphatase_MSA_page_3.jpg]] | |||
[[Image:Pyridoxal_phosphatase_MSA_page_4.jpg]] | |||
'''Structure''' | '''Structure''' | ||
Revision as of 06:43, 3 June 2008
Evolution
File:Pyridoxal phosphatase MSA page 1.jpg File:Pyridoxal phosphatase MSA page 2.jpg File:Pyridoxal phosphatase MSA page 3.jpg File:Pyridoxal phosphatase MSA page 4.jpg
Structure
General Structure of Pyridoxal Phosphatase

PDB
Based on the information provided in the website, Pyridoxal Phosphatase has the following characteristics:
- Pyridoxal Phosphatase is isolated from Homo Sapiens and is expressed in Escherichia Coli.
- Structure is similar to the Pyridoxal Phosphate Phospatase protein
- 1 (A) Chain
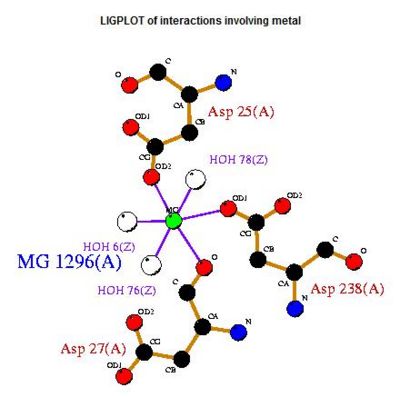
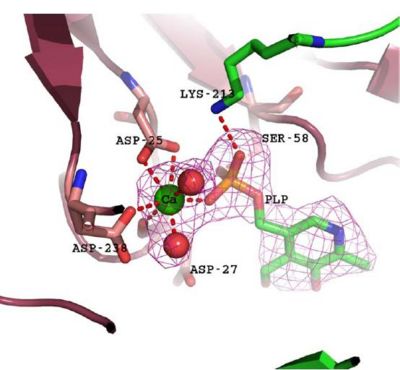
- Consists of Magnesium components
- Resolution of 2.40 angstroms. This means that the number of sidechains in the wrong rotamer is smaller as compared to proteins of a higher resolution (>2.5 angstroms). Other characteristics of proteins of similar resolutions are: (1) many small detectable errors, (2) correct folding, (3) fewer number of errors in the surface loops and (4) visible water molecules and small ligands.
http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/explore.do?structureId=2cfs
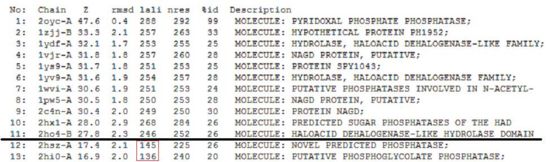
DALI
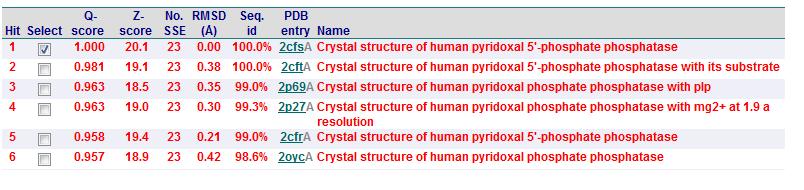
A total of 176 hits were generated, of which only the first 11 (as shown in Fig. 2) were predicted to be significant. The others were rejected on account that their respective nres scores (refer to the red, boxed section) were less than half of Pyridoxal Phosphatase's (nres: 296).
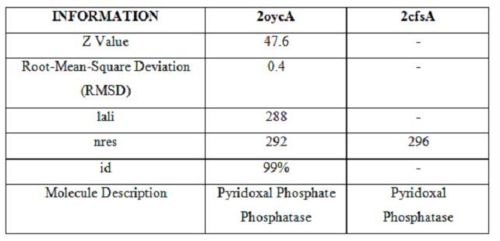
It was noted that none of the hits actually matched 2cfsA. The closest was a Pyridoxal Phosphate Phosphatase (PDB ID 2oycA) which based on the results, was predicted to be highly similar to 2cfsA. Table 1 highlights the similarities between Pyridoxal Phosphatase (2cfsA) and the Pyridoxal Phosphate Phosphatase (2oycA)
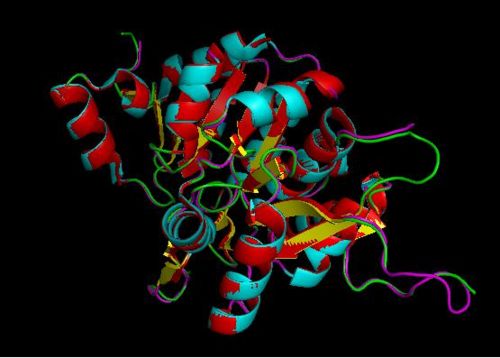
Using the PyMOL software, 2oycA was superimposed against 2cfsA, and both structures, as shown in Fig. 3, are structurally similar.
PDBsum
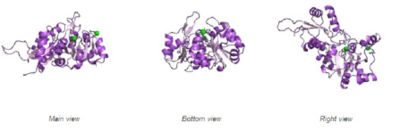
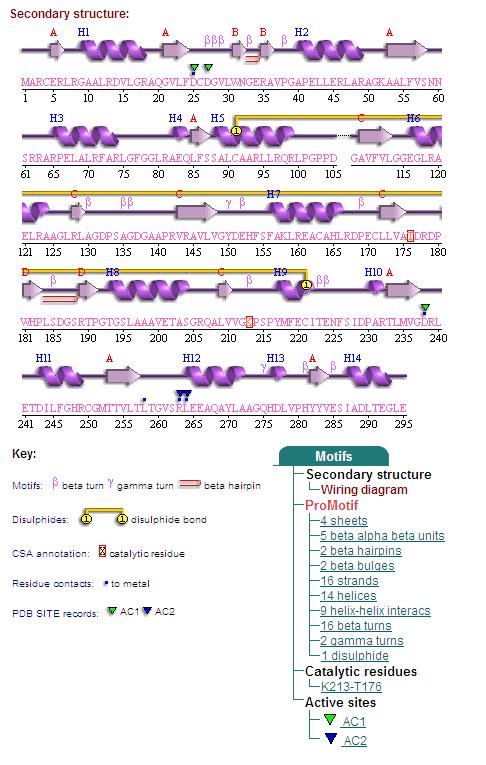
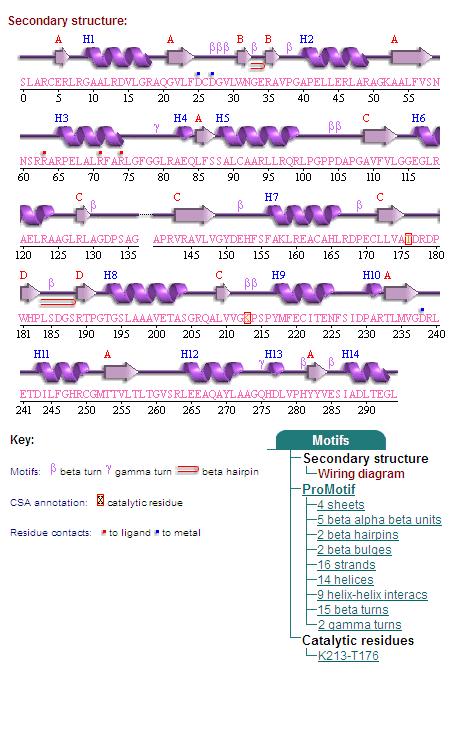
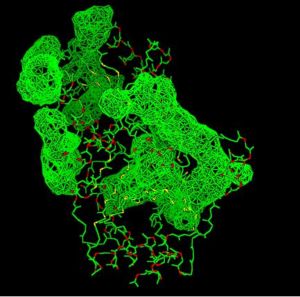
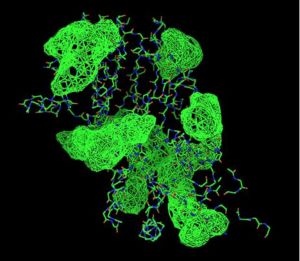
Fig. 4 offers three different views of 2cfsA. The purple chains represent the amino acid chain of 293 amino acids while the green spheres represent the magnesium ions (x2).
By clicking the "Protein chain" link, the user was re-directed to a website containing information pertaining to the secondary structures of both 2cfsA and 2oycA.
Secondary Structures of 2cfsA (L, http://www.ebi.ac.uk/thornton-srv/databases/cgi-bin/pdbsum/GetPage.pl) and 2oycA (R)
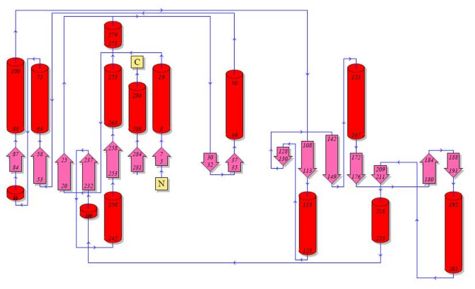
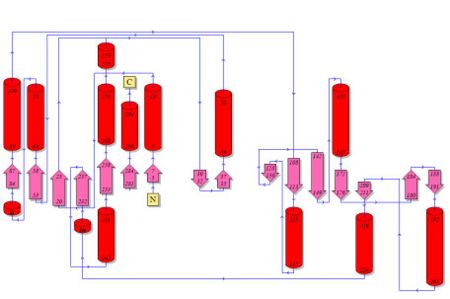
Topology diagrams of 2cfsA (Fig 5.1. http://www.ebi.ac.uk/thornton-srv/databases/cgi-bin/pdbsum/GetPage.pl?pdbcode=2cfs&template=protein.html&r=wiring&l=1&chain=A) and 2oycA (Fig 5.2).
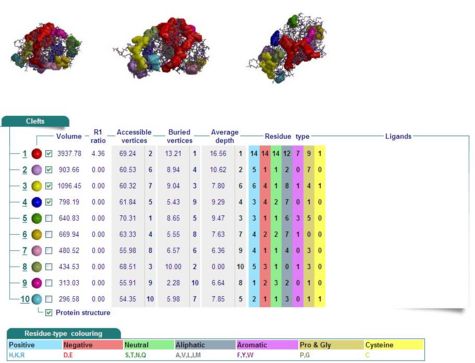
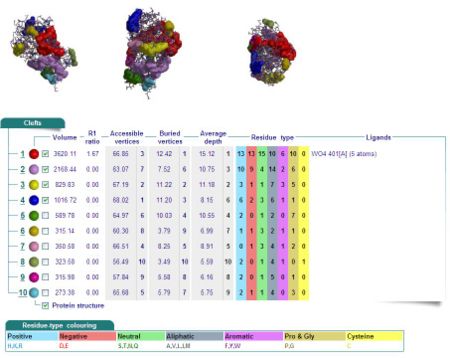
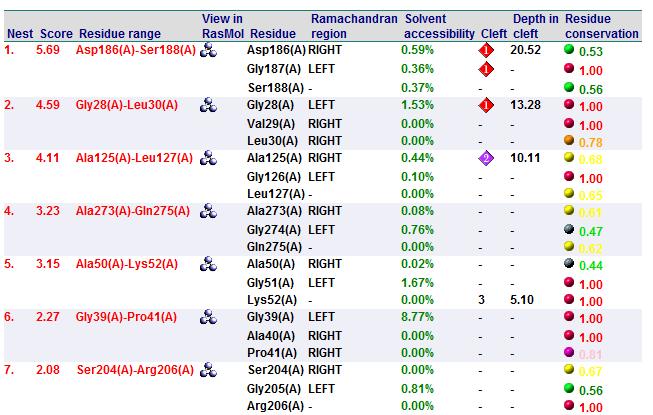
Cleft Analyses of 2cfsA (Fig 6.1. http://www.ebi.ac.uk/thornton-srv/databases/cgi-bin/pdbsum/GetPage.pl?pdbcode=2cfs&template=clefts.html&pdbcode=2cfs&r=speedfill) and 2oycA (Fig 6.2).
Cleft Analysis via PyMol
PROFUNC
Related Protein Sequences in the PDB (SAS)

Matches to existing PDB Structures
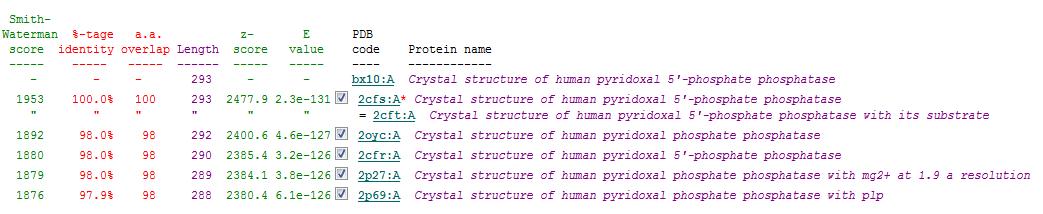
Secondary Structure Matching (SSM)
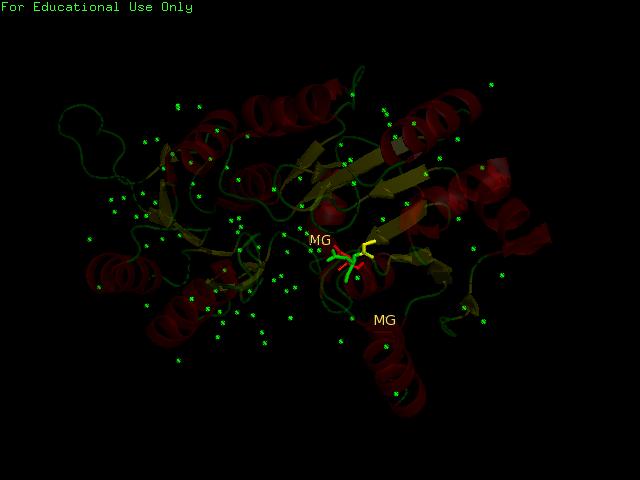
PyMOL generation of potential active site
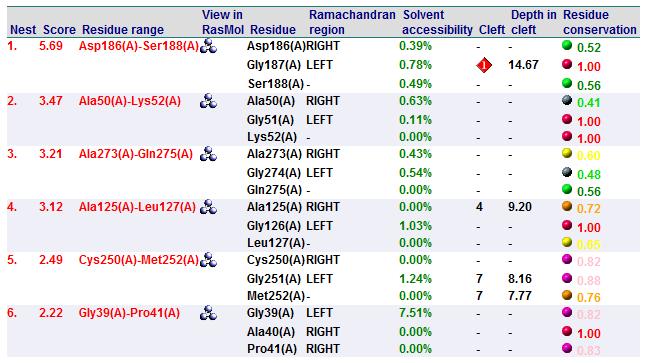
A search on 2oycA was also carried out via PROFUNC, and consistency in the results confirmed that 2cfsA and 2oycA were indeed structurally similar. This lends weight to the original hypothesis that they could be functionally related. In fact, based on the Nest Analysis method, 2oycA was observed to be sharing a large number of active sites. The results of the Nest Analysis (2oycA) are as shown below. Notice the similarities between the active sites of both 2oycA and 2cfsA.
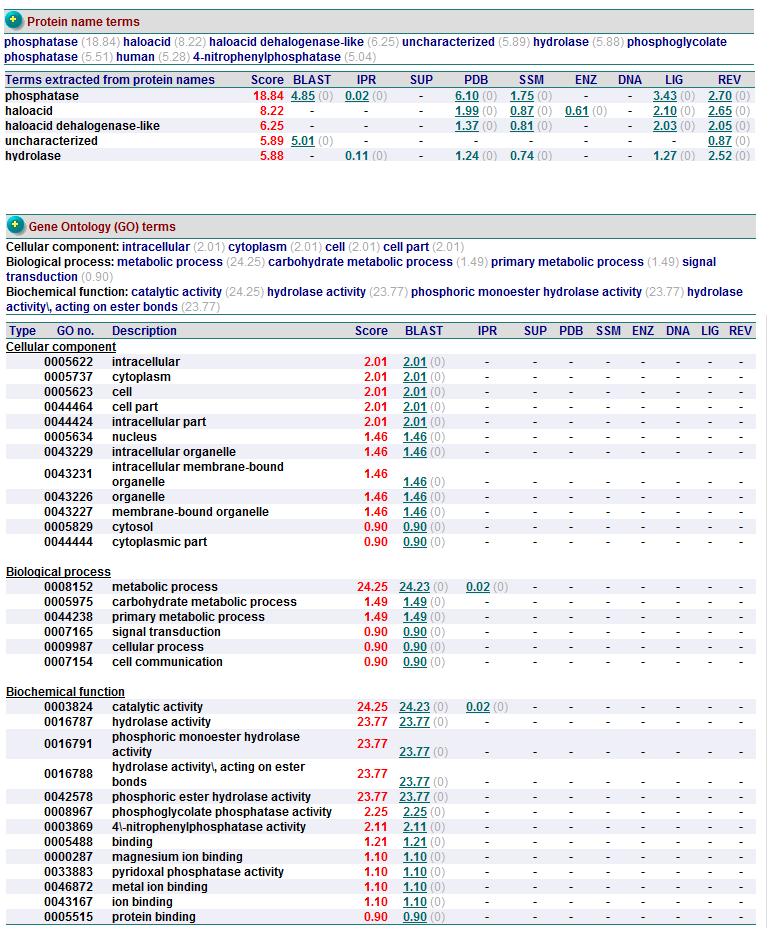
In addition, the predicted function of 2oycA was similar to 2cfsA.
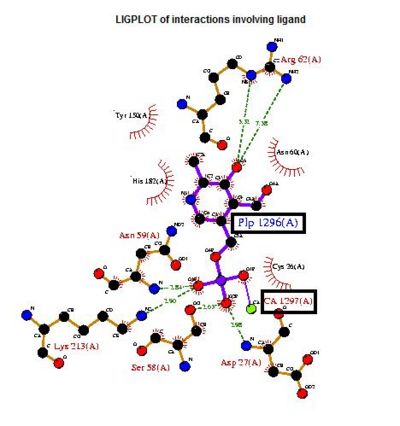
Based on the above-mentioned results, it was concluded that 2cfsA, 2cftA and 2oycA were structurally similar, and that further functional studies could indeed uncover the function of the protein-of-interest: 2cfsA
Function