Role in Human: Difference between revisions
From MDWiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<font size = "4">'''Role in | <font size = "4">'''Role in Human'''</font> | ||
* OMIM | |||
** Haloacid dehalogenase-like hydrolase domain | |||
** Gene map locus 20p11 | |||
[[Image:Document2_01.png]] | |||
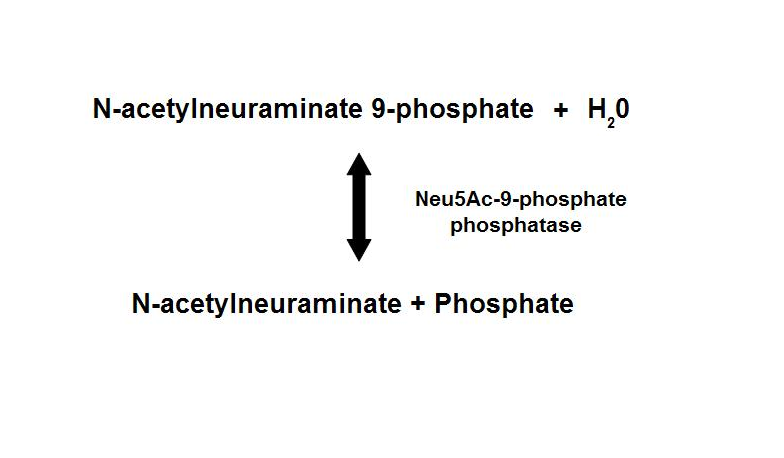
Dephosphorylation of Neu5Ac-9-P is a reversible reaction with an end product of Neu5Ac (sialic acid) and a free phosphate. | |||
* Main form of sialic acid in vertebrates | |||
** Important roles in protein-protein and cell-cell recognition | |||
[[HAD|Next Page]] | |||
Latest revision as of 01:39, 12 June 2007
Role in Human
- OMIM
- Haloacid dehalogenase-like hydrolase domain
- Gene map locus 20p11
Dephosphorylation of Neu5Ac-9-P is a reversible reaction with an end product of Neu5Ac (sialic acid) and a free phosphate.
- Main form of sialic acid in vertebrates
- Important roles in protein-protein and cell-cell recognition