Ssu72 Results: Difference between revisions
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
image:Figure_2.png|'''Figure 2''': PubMed results for human Ssu72 protein. | image:Figure_2.png|'''Figure 2''': PubMed results for human Ssu72 protein. | ||
image:Figure_3.png|'''Figure 3''': Expression profile for the human Ssu72 protein. | image:Figure_3.png|'''Figure 3''': Expression profile for the human Ssu72 protein. | ||
image:Human Ssu72 BLAST result.PNG|'''Figure 4''': | image:Human Ssu72 BLAST result.PNG|'''Figure 4''': Multiple sequence alignment of Drosophila Ssu72 (query) and Human Ssu72 (sbjct) from BLAST result. | ||
</gallery></center> | </gallery></center> | ||
Revision as of 12:40, 11 June 2009
Function
BLAST results
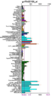
Running a protein BLAST search on the Drosophila Ssu72 protein returned a large number of highly relevant (bit score > 200) sequences that were of a very similar length (see Figure 1). However, the first 27 of those sequences were not considered relevant for a number of reasons. For instance, some were merely homologous proteins in other closely related Drosophila species that had been identified in a similar manner to this one and for which there were no PubMed publications available and thus no information that could be used to easily infer function. Other had not been functionally characterised by experimentation or structural analysis, because they had been identified by high-throughput sequencing. Some BLAST hits were labelled as hypothetical proteins and therefore not necessarily even protein coding or biologically present. The first relevant protein identified was 'SSU72 RNA polymerase II CTD phosphatase homolog (S. cerevisiae)', the human Ssu72 protein, for which there were a small number of articles available on PubMed (see Figure 2), as well as expression data from SymAtlas (see Figure 3). This protein was also found to have
Literature review
The function of the human Ssu72 protein, for which there exist a number of mammalian homologues, was first thought to be . Therefore, our candidate protein, Drosophila Ssu72, was analysed at the level of its amino acid sequence to determine if this function could be conserved. It
Evolution
Heading
Structure
Heading
Abstract | Introduction | Results | Discussion | Conclusion | Method | References