COASY results: Difference between revisions
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
|Cell 1 || Cell 2 || Cell 3 | |Cell 1 || Cell 2 || Cell 3 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | |Pattern-ID: GLYCOSAMINOGLYCAN PS00002 PDOC00002 | ||
| | |Pattern-DE: Glycosaminoglycan attachment site | ||
| | |Pattern: SG.G | ||
|Position: 84 SGSG | |||
|Pattern-ID: PKC_PHOSPHO_SITE PS00005 PDOC00005 | |||
|Pattern-DE: Protein kinase C phosphorylation site | |||
|Pattern: Pattern: [ST].[RK] | |||
|Position: 3 SDK | |||
|Position: 52 SFR | |||
|Position: 86 SGK | |||
|Pattern-ID: CK2_PHOSPHO_SITE PS00006 PDOC00006 | |||
|Pattern-DE: Casein kinase II phosphorylation site | |||
|Pattern: [ST].{2}[DE] | |||
|Position: 39 SHNE | |||
|Position: 251 TLWE | |||
|Position: 260 SQVE | |||
|Pattern-ID: MYRISTYL PS00008 PDOC00008 | |||
|Pattern-DE: N-myristoylation site | |||
|Pattern: G[^EDRKHPFYW].{2}[STAGCN][^P] | |||
|Position: 82 GISGSG | |||
|Position: 222 GLSEAA | |||
|Pattern-ID: ATP_GTP_A PS00017 PDOC00017 | |||
|Pattern-DE: ATP/GTP-binding site motif A (P-loop) | |||
|Pattern: [AG].{4}GK[ST] | |||
|Position: 82 GISGSGKS | |||
|Pattern-ID: UPF0038 PS01294 PDOC00996 | |||
|Pattern-DE: Uncharacterized protein family UPF0038 signature | |||
|Pattern: G.[LI].R.{2}L.{4}F.{8}[LIV].{5}P.[LIV] | |||
|Position: 136 GTINRKVLGSRVFGNKKQMKILTDIVWPVI | |||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 13:31, 9 June 2007
Structure of Coenzyme A Synthase
Conezyme A Synthase is structurally composed of seven strands, eleven helices and thirteen beta turns (EMBL EBI, 2005) (see Figure 1). Analysis of structurally related proteins (Holm & Sander, 1993) showed a trend for transferase (RCSB, 2007) class proteins with Rossmann class folds (Rossmann, 1973). The Rossmann topologies of fold’s are an alpha-beta class fold that forms a three or more layer beta strand sandwich alternating with alpha helices (beta-alpha-beta-alpha-beta). PFAM classification placed these into either the Cytidylyltransferase or Dephospho-CoA kinase familes, matching the two domains of Coenzyme A Synthase. Those classified under the Dephospho-CoA kinase type were commonly of the P-loop containing nucleotide triphosphate hydrolases (Sanger Institute, 2005) homology whilst those classified as Cytidylyltransferase were of the Tyrosol-Transfer RNA Synthetase (Sanger Institute, 2005). As the majority of the structurally related proteins identified contained the DPCK domain solely, and the motif for a P-loop (Table 1) was identified in the Conzyme A Synthase sequence (Bairoch, Bucher, & Hofmann, 1997) it is suggested that Coenzyme A Synthase is also of the P-loop containing nucleotide triphosphate hydrolases homology of folds.
Table 1
| Cell 1 | Cell 2 | Cell 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pattern-ID: GLYCOSAMINOGLYCAN PS00002 PDOC00002 | Pattern-DE: Glycosaminoglycan attachment site | Pattern: SG.G | Position: 84 SGSG | Pattern-ID: PKC_PHOSPHO_SITE PS00005 PDOC00005 | Pattern-DE: Protein kinase C phosphorylation site | Pattern: Pattern: [ST].[RK] | Position: 3 SDK | Position: 52 SFR | Position: 86 SGK | Pattern-ID: CK2_PHOSPHO_SITE PS00006 PDOC00006 | Pattern-DE: Casein kinase II phosphorylation site | Pattern: [ST].{2}[DE] | Position: 39 SHNE | Position: 251 TLWE | Position: 260 SQVE | Pattern-ID: MYRISTYL PS00008 PDOC00008 | Pattern-DE: N-myristoylation site | Pattern: G[^EDRKHPFYW].{2}[STAGCN][^P] | Position: 82 GISGSG | Position: 222 GLSEAA | Pattern-ID: ATP_GTP_A PS00017 PDOC00017 | Pattern-DE: ATP/GTP-binding site motif A (P-loop) | Pattern: [AG].{4}GK[ST] | Position: 82 GISGSGKS | Pattern-ID: UPF0038 PS01294 PDOC00996 | Pattern-DE: Uncharacterized protein family UPF0038 signature | Pattern: G.[LI].R.{2}L.{4}F.{8}[LIV].{5}P.[LIV] | Position: 136 GTINRKVLGSRVFGNKKQMKILTDIVWPVI |
Figure 1
The secondary structure of Mus musculus with indicated ligand interaction sites (EMBL EBI, 2005).
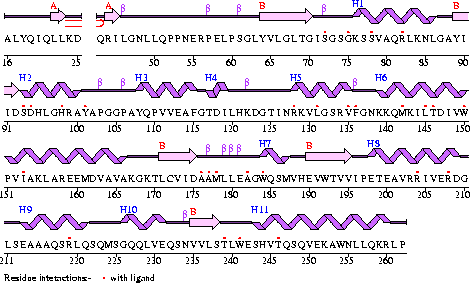
Figure 2
Structural alignment of structurally related proteins to Mus. musculus Coenzyme A Synthase
Localisation Expression of Coenzyme A Synthase
Sequence Conservation of Coenzyme A Synthase
Structural Elements and Functional Binding Sites of Coenzyme A Synthase
Abstract | Introduction | Results | Discussion | Conclusion | Method | References